1.介绍
BGAN的全称是Boundary Seeking GAN,它的中文翻译是:基于边界寻找的gan,那么这个边界指的是谁呢?一般而言,判别器的loss稳定在0.5的时候,生成图片的效果是最好的,而这个边界指代的就是0.5
2.模型结构
个人认为gan的模型结构不是那么重要,重要的是它的损失函数和它所用到的一些技巧性东西,很多论文,就不画结构图在上面,本篇论文也是这样干的,因此我也不放了。
3.模型特点
BGAN与原始gan(GAN 简介与代码实战_天竺街潜水的八角的博客-CSDN博客)的主要区别在于损失函数
对于上面原始gan损失函数,当固定G的时候,可以得到最优D


当G对应着最优D的时候,真实分布Pdata(x)可以被整理出下面公式,但我们可以通过调整生成分布、G和D来得到真实分布,但这里有一个问题,其实我们训练gan的时候,很难得到最优D,所以此假设,在大部分情况下是不成立的。
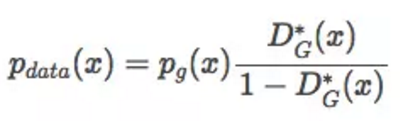
为了得到最优D,我们把损失函数改成下面公式,当D(x)=0.5的时候,G最优。
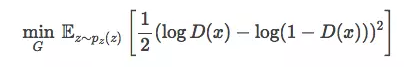
4.代码实现keras
class BGAN(): """Reference: https://wiseodd.github.io/techblog/2017/03/07/boundary-seeking-gan/""" def __init__(self): self.img_rows = 28 self.img_cols = 28 self.channels = 1 self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels) self.latent_dim = 100 optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5) # Build and compile the discriminator self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator() self.discriminator.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer=optimizer, metrics=['accuracy']) # Build the generator self.generator = self.build_generator() # The generator takes noise as input and generated imgs z = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,)) img = self.generator(z) # For the combined model we will only train the generator self.discriminator.trainable = False # The valid takes generated images as input and determines validity valid = self.discriminator(img) # The combined model (stacked generator and discriminator) # Trains the generator to fool the discriminator self.combined = Model(z, valid) self.combined.compile(loss=self.boundary_loss, optimizer=optimizer) def build_generator(self): model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(256, input_dim=self.latent_dim)) model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)) model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)) model.add(Dense(512)) model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)) model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)) model.add(Dense(1024)) model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)) model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)) model.add(Dense(np.prod(self.img_shape), activation='tanh')) model.add(Reshape(self.img_shape)) model.summary() noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,)) img = model(noise) return Model(noise, img) def build_discriminator(self): model = Sequential() model.add(Flatten(input_shape=self.img_shape)) model.add(Dense(512)) model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)) model.add(Dense(256)) model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)) model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')) model.summary() img = Input(shape=self.img_shape) validity = model(img) return Model(img, validity) def boundary_loss(self, y_true, y_pred): """ Boundary seeking loss. Reference: https://wiseodd.github.io/techblog/2017/03/07/boundary-seeking-gan/ """ return 0.5 * K.mean((K.log(y_pred) - K.log(1 - y_pred))2) def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50): # Load the dataset (X_train, _), (_, _) = mnist.load_data() # Rescale -1 to 1 X_train = X_train / 127.5 - 1. X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3) # Adversarial ground truths valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1)) fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1)) for epoch in range(epochs): # --------------------- # Train Discriminator # --------------------- # Select a random batch of images idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size) imgs = X_train[idx] noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, self.latent_dim)) # Generate a batch of new images gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise) # Train the discriminator d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(imgs, valid) d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(gen_imgs, fake) d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake) # --------------------- # Train Generator # --------------------- g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch(noise, valid) # Plot the progress print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc.: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1], g_loss)) # If at save interval => save generated image samples if epoch % sample_interval == 0: self.sample_images(epoch) def sample_images(self, epoch): r, c = 5, 5 noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c, self.latent_dim)) gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise) # Rescale images 0 - 1 gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5 fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c) cnt = 0 for i in range(r): for j in range(c): axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt, :,:,0], cmap='gray') axs[i,j].axis('off') cnt += 1 fig.savefig("images/mnist_%d.png" % epoch) plt.close()讯享网

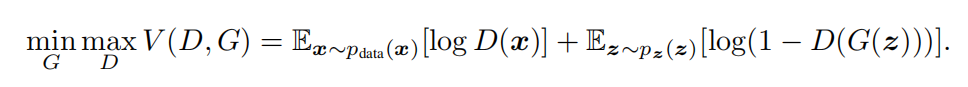
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容,请联系我们,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://51itzy.com/kjqy/47433.html