gRpc入门和springboot整合
一、简介
1、gprc概念
gRpc是有google开源的一个高性能的pc框架,Stubby google内部的rpc,2015年正式开源,云原生时代一个RPC标准。
tips:异构系统,就是不同编程语言的系统。
2、grpc核心设计思路
grpc核心设计思路 1. 网络通信 --> grpc自己封装网络通信的部分,提供多种语言的网络通信的封装(java(netty),c,go)的支持异构语言。 2. 协议 --> http2协议,传输数据,支持二进制。支持双向流(双工)。连接的多路复用(NIO) 3. 序列化 --> 基于文本Json,基于二进制(java原生序列化方式,Thrift二进制序列化,压缩二进制序列化) protobuf(protocol buffers)google开源的一种序列化方式。 dubbo也可以用protobuf。 时间效率和空间效率是Json的3---5倍。 定义了一套,IDL语言。 4.代理的创建 --> 让调用者像调用本地方法那样,去调用远端的服务方法一样。 stub. 讯享网
3、gRpc和protobuf的区别
grpc是rpc框架。
protobuf是一种序列化方式
4、gRpc与ThrifRpc区别
讯享网 共性:支持异构语言的 RPC 区别: 1. 网络通信 Trift TCP 专属协议 grpc http2 2. 性能角度,thrift Rpc效率高于gRpc. 3. gRpc 大厂背书(google),云原生时代 合作更好 集成更多,所以grpc应用更广泛
5、gRpc的好处
- 高效的进行进程间通信。
- 支持多种语言 。原生支持,C GO Java实现。c语言版本上扩展,c++,c#,node JS,python,ruby,php (二等公民)
- 支持多平台运行。 Linux Andriod IOS MacOS Windows
- gRpc序列化方式采用protobuf,效率高
- 使用http2协议
- 大厂背书
二、http2.0协议
1、回顾 http1.x 协议
1.1、http1.0 协议
- 请求响应的模式。
- 短连接协议(无状态协议)。建立在tcp(长连接)上的,http主动断开连接(之前设备不好,主动断开)。
- 传输数据文本结构
- 单工,无法实现服务端推送。
- 变相实现服务推送,(采用客户端轮询)
1.2、http1.1 协议
- 请求相应的模式
- 有限的长连接(保持一段时间)
- 只能通过升级的方式,websocket协议,实现服务器想客户端推送。不属于http1.1的能力
1.3、总结http1.x协议特性:
- 传输数据文本格式,可读性好但是效率差。
- 本质上http1.x协议,无法实现双工通信。
- 资源的请求。需要发送多次请求,建立多个连接才可以完成。分流(静态资源分离,cdn缓存加速)
2、HTTP2.0协议
- Http2.0协议是一个二进制协议,效率高于Http1.x协议,可读性差。
- 可以实现双工通信
- 一个连接可以请求多个数据。【多路复用】
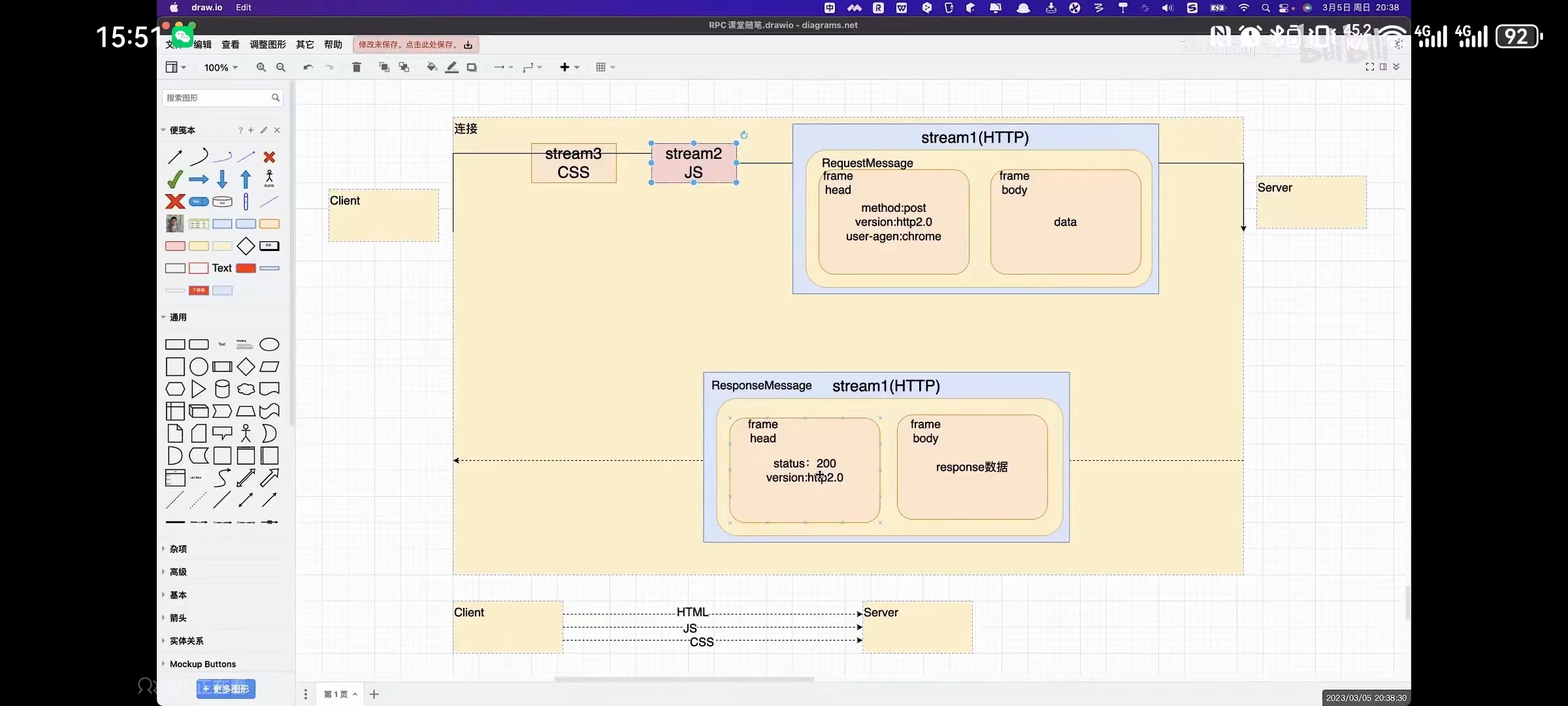
3、HTTP2.O协议的三个概念
- 数据流 Stream
- 消息 message
- 帧 frame
一个连接,有多个数据流。Stream.
3.1、requestMessage
一个数据流,有request Message.
Message,里面有frame.
第一个frame,对应的就是header。
- method:post
- version:http2.0
- user-agent:chrome
第二个frame,是body
- data
如果get,就是一个frame帧。没有data,body。
3.1、responseMessage
第一个frame,对应的就是head。
- status: 200
- version:http2.0
第二个frame,是body
- response数据
4、其他的相关概念
4.1、数据流的优先级
1. 数据流的优先级:可以为不同的Stream设置权重,来限制不同流的顺序。 1. 流控:client发送数据太快了,server处理不过来,通知client暂停数据的发送。 三、Protocol Buffers [protobuf]
1、简介
- protobuf是一种与编程语言无关【IDL】,与具体的平台无关【OS】。他定义的中间语言,可以方便,在Client和server之间进行RPC的数据传输。
- protobuf
- protobuf 2
- protobuf 3
目前主流应用的都是protobuf3.
- protobuf主要安装protobuf的编译器,编译器目的,可以把protobuf的IDL语言,转换成具体某一种开发语言。
2、protobuf编译器安装
github上.
https://www.github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases
建议,64位,v3.19.6,是一个exe文件。
讯享网windows版本 1.直接解压缩,放置在一个特定的目录下面 2.直接配置环境变量 path protoc --version mac版本 brew install protobuf
3、protobuf IDEA插件
IDEA 新版本。原生支持,protocol Buffers.
- 2021.2版本后面的新版本,IDEA内置了Protobuf插件,和gRPC插件,都是默认勾选的。
- 2021.2版本之前的老版本,可以选装第三方protobuf插件。
- 二者不能共存
4、与Java语言相关的语法
#后续protobuf生成的java代码 一个源文件还是多个源文件 xx.java option java_multiple_files = false; //生成一个源文件。 #指定protobuf生成的类,放置在哪个包中 option java_package = "com.suns"; //java相关 #指定的protobuf生成的外部类的名字(管理内部类【内部类才是真正开发使用】,相当于文件夹) option java_outer_classname = "UserService"; 外部类.内部类. 5、逻辑包
讯享网#对于protobuf对于文件内容的管理 package xxx;
6、导入
UserService.proto OrderService.proto imort "xxx/UserService.proto" 7、protobuf 基本类型介绍
- 描绘RPC服务,远端接口。 Service(trift) gRpc也叫Service
- 结构体Struct(thrift) ; message(gRpc)
主要是看service和message如何定义。
protobuf的类型
https://www.protobuf.dev/programing-guides/proto3/
Scalar Value Types
A scalar message field can have one of the following types – the table shows the type specified in the .proto file, and the corresponding type in the automatically generated class:
| .proto Type | Notes | Java/Kotlin Type[1] |
|---|---|---|
| double | double | |
| float | float | |
| int32 | Uses variable-length encoding. Inefficient for encoding negative numbers – if your field is likely to have negative values, use sint32 instead. | int |
| int64 | Uses variable-length encoding. Inefficient for encoding negative numbers – if your field is likely to have negative values, use sint64 instead. | long |
| uint32 | Uses variable-length encoding. | int[2] |
| uint64 | Uses variable-length encoding. | long[2] |
| sint32 | Uses variable-length encoding. Signed int value. These more efficiently encode negative numbers than regular int32s. | int |
| sint64 | Uses variable-length encoding. Signed int value. These more efficiently encode negative numbers than regular int64s. | long |
| fixed32 | Always four bytes. More efficient than uint32 if values are often greater than 228. | int[2] |
| fixed64 | Always eight bytes. More efficient than uint64 if values are often greater than 256. | long[2] |
| sfixed32 | Always four bytes. | int |
| sfixed64 | Always eight bytes. | long |
| bool | boolean | |
| string | A string must always contain UTF-8 encoded or 7-bit ASCII text, and cannot be longer than 232. | String |
| bytes | May contain any arbitrary sequence of bytes no longer than 232. | ByteString |
8、枚举
讯享网enum SEASON{ SPRING = 0; SUMMER = 1; } 枚举的值 必须是0开始。
9、消息Message
9.1、基本定义
message LoginRequest{ String username = 1;//代表编号。不是value singular String password = 2; int32 age = 3 ; } 9.2、编号问题:
从1开始,到2^29-1,注意19000-19999 这几个编号不能用。这是protobuf自己保留的区间。
消息
讯享网- singular : 修饰messgae字段,这个字段只能是0个或1个 (默认关键字)0:null, 1:"" - reapeated : 这个字段返回值是多个;等价于java List message Result{ string content = 1; reapeated string stutas = 2; //这个字段返回值是多个;等价于java List; Protobuf, 生成一个get方法: getStatusList()->List }
9.3、protobuf [gRpc] 可以定义多个消息
message LoginRequest{ ... } message LoginResponse{ ... } 9.4、消息可以嵌套
讯享网message SearchResponse{ message Result{ string url = 1; string title =2; } string xxx = 1; string yyy = 2; Result ppp = 3;//内部。上面是定义message } 其他人调用:SearchResponse.Result message AAA{ string xxx = 1; SearchResponse.Result yyy = 2; }
9.5、oneof [其中一个]
message SimpleMessage{ //可取值,要么是string要么是int32 oneof test_oneof{ string name = 1; int32 age =2 } test_oneof xxx; } 9.6、服务
讯享网service HelloService{ rpc hello(HelloRequest) returns(HelloResponse){} } # 里面可以定义多个服务方法 # 定义多个服务接口 #gRpc 服务 4个服务方式.
4、第一个gRpc开发
4.1、项目结构
1. xxxx-api 模块 定义protobuf idl语言 并且通过命令创建具体的代码,后续client,server引入使用。 1. message 2. service 2. xxxx-server 模块 1.实现api模块中定义的服务接口 2.发布gRpc服务(创建服务器程序) 3. xxxx-client模块 1. 创建服务端stub(代理) 2. 基于代理(stub)RPC调用 4.2、api模块 grpc-api
1、proto文件 书写protobuf的IDL
2、protoc命令 把proto文件的IDL转换成编程语言。
讯享网#--java_out 表示 生成java --go_out,表示生成go #--java_out=/xxx/xxx /xxx/xxx 表示位置 # /xxx/xxx/xx.proto 基于什么IDL的。 这个是源文件。 protoc --java_out=/xxx/xxx /xxx/xxx/xx.proto
3、实战】maven插件 进行protobuf IDL文件的编译,并把它放置IDEA具体位置。
4、github上有开源的插件。g
http://www.github.com/grpc/grpc-java 讯享网pom.xml <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>io.grpc</groupId> <artifactId>grpc-netty-shaded</artifactId> <version>1.57.2</version> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>io.grpc</groupId> <artifactId>grpc-protobuf</artifactId> <version>1.57.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>io.grpc</groupId> <artifactId>grpc-stub</artifactId> <version>1.57.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <!-- necessary for Java 9+ --> <groupId>org.apache.tomcat</groupId> <artifactId>annotations-api</artifactId> <version>6.0.53</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> 生成功能 <build> <extensions> <extension> <groupId>kr.motd.maven</groupId> <artifactId>os-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>1.7.1</version> </extension> </extensions> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.xolstice.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>protobuf-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>0.6.1</version> <configuration> protoc命令 生成message信息 <protocArtifact>com.google.protobuf:protoc:3.22.3:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</protocArtifact> <pluginId>grpc-java</pluginId> protoc命令 生成service <pluginArtifact>io.grpc:protoc-gen-grpc-java:1.57.2:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</pluginArtifact> </configuration> <executions> <execution> <goals> <goal>compile</goal> <goal>compile-custom</goal> </goals> </execution> </executions> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
${os.detected.classifier} maven内置变量;
获取当前 操作系统类型 windows -x86.
goal:maven goal;
compile;
compile-custom
5、源文件如下:
syntax = "proto3"; option java_multiple_files = false; option java_package = "com.lizy"; option java_outer_classname = "HelloProto"; /* 命名Hello.proto,outer_classname = HelloProto IDL文件 目的 发布RPC服务,service---> message message<--------- 先定义message */ message HelloRequest{ string name = 1; } message HelloResponse{ string result = 1; } /* 再定义service 需要让 protobuf转换 IDL语言。 */ service HelloService{ rpc hello(HelloRequest) returns (HelloResponse){} } 这个字体蛮好看的
霞鹜文楷
使用 no meirye ui version 3.0.0
讯享网reg save "HKCU\Control Panel" .\reset_font.reg /y https://github.com/Tatsu-syo/noMeiryoUI
6、使用mavenHelper插件
可以使用ctrl+alt+r 快捷键导入。

7、使用maven的plugins中protobuf-maven-plugin插件
生成的文件会放在target里面。
- 需要执行两个命令
- compile
- compile-custom
- 然后再去手工移动生成的文件
过于麻烦。
8、从实战出发。
问题1:需要执行两个命令
解决:maven new goal,生成一个合并的命令
mvn xxx xxx;
Run maven goal;
new maven goal 点击需要的goal,点击两个,就可以直接有两个一起。 问题2:手工移动生成的文件太过麻烦
解决:在pom.xml文件中增加两行outputDirectory,clearOutputDirectory
讯享网 <configuration> <!-- protoc命令 生成message信息--> <protocArtifact>com.google.protobuf:protoc:3.22.3:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</protocArtifact> <pluginId>grpc-java</pluginId> <!-- protoc命令 生成service--> <pluginArtifact>io.grpc:protoc-gen-grpc-java:1.57.2:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</pluginArtifact> <outputDirectory>${basedir}/src/main/java</outputDirectory> <!-- false 追加式生成--> <clearOutputDirectory>false</clearOutputDirectory> </configuration>

ctr+o 重写父类方法。
在 gRPC 中,BlockingStub, FutureStub, 和 Stub 是用于与 gRPC 服务进行交互的不同接口。它们的主要区别在于它们提供的方法调用的方式。 BlockingStub: BlockingStub 是 gRPC 提供的阻塞式接口。使用此接口,调用远程服务是阻塞的,也就是说,调用者必须等待服务器的响应才能继续执行。在调用方法后,你需要使用 .get() 方法来阻塞并等待结果。这是一个非常直接且易于理解的接口,但需要调用者等待,可能不适合处理大量并发的请求。 例如: java BlockingGrpc.newBlockingStub(channel).someRpc(request).get(); FutureStub: FutureStub 也是阻塞式的接口,但与 BlockingStub 不同的是,它返回一个 Future 对象,这个对象表示一个尚未完成的计算或操作。你可以使用 Future.get() 来阻塞并等待结果,或者注册一个回调函数来在结果可用时自动获取。这种方式比 BlockingStub 更灵活,因为它允许你在等待结果的同时执行其他任务。 例如: java Futures.getUnchecked(future = asyncStub.someRpc(request)); Stub: 与前两者不同,Stub 是一个非阻塞的接口,它使用异步回调方式。当调用远程服务时,它不会立即返回结果,而是通过回调函数将结果传递给调用者。这种方式可以处理大量并发请求,并且可以更有效地利用系统资源。然而,与前两者相比,它可能需要更多的代码和更复杂的逻辑来处理异步回调。 例如: java channel.io().Schedulers.scheduleDirect(() -> { someRpc(request, new Callback() { @Override public void onSuccess(Object result) { // handle the result } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) { // handle the error } }); }); 在选择使用哪种接口时,应根据你的应用需求和性能要求来决定。如果你需要简单直接的接口并且不介意阻塞等待结果,那么 BlockingStub 可能是最好的选择。如果你需要更灵活的处理方式并且愿意编写更多的代码来处理异步回调,那么 FutureStub 或 Stub 可能更适合你。 4.3、service模块 grpc-service
1、创建业务service
创建service模块,service类:HelloServiceImpl
业务端代码:
讯享网package com.lizy.service; import com.lizy.HelloProto; import com.lizy.HelloServiceGrpc; import io.grpc.stub.StreamObserver; public class HelloServiceImpl extends HelloServiceGrpc.HelloServiceImplBase {
/ * 传统ssm * 1. 接受client的提交参数 request.getParameter() * 2. 业务处理 service+dao 调用对应的业务功能 * 3. 提供返回值 * @param request request * @param responseObserver responseObserver */ @Override public void hello(HelloProto.HelloRequest request, StreamObserver<HelloProto.HelloResponse> responseObserver) {
//1. 接受client的请求参数 String name = request.getName(); //2. 业务处理 todo 基本处理这一块。 System.out.println("name parameter: "+ name); //3. 封装响应 //3.1 创建响应对象的构造着 HelloProto.HelloResponse.Builder builder = HelloProto.HelloResponse.newBuilder(); //3.2 填充数据 builder.setResult("hello method invoke ok"); //3.3 封装响应 HelloProto.HelloResponse helloResponse = builder.build(); //处理后的响应的消息,通过网络回传 client responseObserver.onNext(helloResponse); //通知client响应已经结束 --> 标志 responseObserver.onCompleted(); } }
2、创建服务端
服务端代码:
public class GrpcServer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, IOException {
//1. 绑定端口 ServerBuilder<?> serverBuilder = ServerBuilder.forPort(9000); //2. 发布服务 serverBuilder.addService(new HelloServiceImpl()); //多个服务就add多个 // serverBuilder.addService(new UserServiceImpl()); //3. 创建服务对象 Server server = serverBuilder.build(); server.start(); server.awaitTermination(); } } tips:pom.xml 父依赖 可以打印日志。
讯享网 <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId> <version>1.7.32</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId> <artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId> <version>1.2.9</version> </dependency> </dependencies> 版本太高会有问题。
4.4、client模块 grpc-client
1、client通过代理对象完成远端对象的调用。
package com.lizy; import io.grpc.ManagedChannel; import io.grpc.ManagedChannelBuilder; public class GrpcClient1 { public static void main(String[] args) { //1. 创建通信的管道 ManagedChannel managedChannel = ManagedChannelBuilder.forAddress("localhost", 9000).usePlaintext().build(); //2. 获得代理对象 stub 存根。 try { HelloServiceGrpc.HelloServiceBlockingStub helloService = HelloServiceGrpc.newBlockingStub(managedChannel); //3.完成RPC调用 //3.1 准备参数 HelloProto.HelloRequest.Builder builder = HelloProto.HelloRequest.newBuilder(); builder.setName("李君临"); HelloProto.HelloRequest helloRequest = builder.build(); //3.2 进行功能rpc调用,获取响应的内容 HelloProto.HelloResponse helloResponse = helloService.hello(helloRequest); String result = helloResponse.getResult(); System.out.println("result = "+result); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { managedChannel.shutdown(); } } } 注意事项
client会去监听【grpc做的】 responseObserver.onCompleted();
讯享网//处理后的响应的消息,通过网络回传 client responseObserver.onNext(helloResponse); //通知client响应已经结束 --> 标志 ;通知client 整个服务结束,底层返回标记。 responseObserver.onCompleted(); requestObserver.onNext(helloRequest1); requestObserver.onCompleted();
5、gRpc的四种通信方式
5.1、四种通信方式
- 简单rpc 一元rpc(unary RPC)
- 服务端流式RPC( Server Streaming RPC)
- 客户端流式RPC(Client Streaming RPC)
- 双向流RPC(Bi-directional Stream RPC)
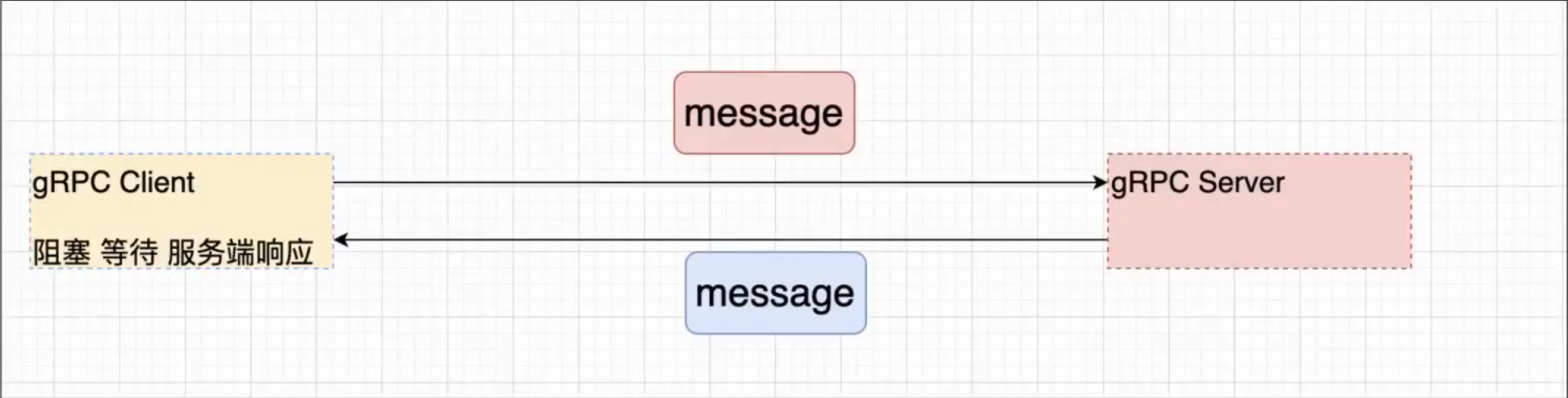
5.2、简单RPC(一元RPC)
上面第一个RPC程序,实际上就是一元RPC
1、特点
- 当client发起调用后,提交数据,并且等待服务端响应。
- 开发过程中,主要采用就是一元RPC的这种通信方式。
2、语法
service HelloService{ rpc hello(HelloRequest) returns (HelloResponse){} } 5.3、服务端流式RPC
一个请求对象,服务端可以回传多个结果对象。
1、特点
一个请求对象,服务端可以回传多个结果对象。
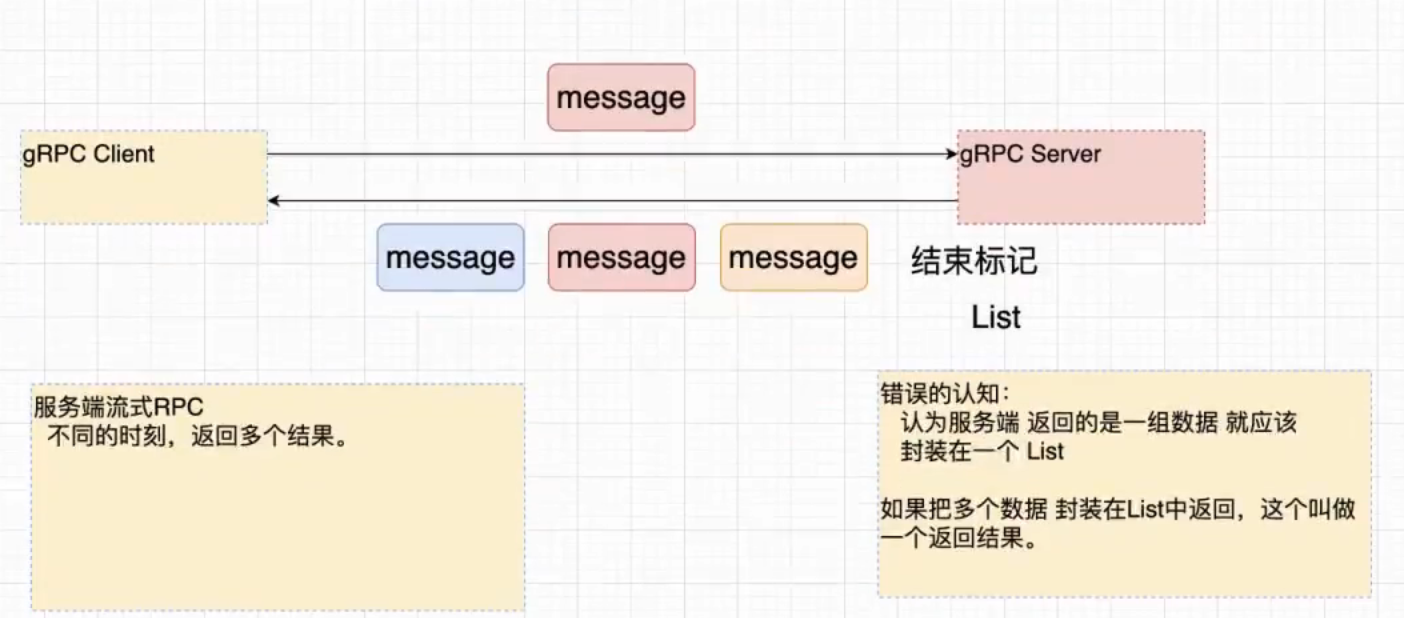
2、使用场景
讯享网client --------> server 股票标号 <---------- 某一个时刻的 股票的行情
3、语法
返回值,增加stream 关键字
service HelloService{ rpc hello(HelloRequest) returns (stream HelloResponse){} //服务端流式RPC rpc hello(HelloRequest1) returns (HelloResponse1){} //一元RPC } 4、开发实践
4.1、代码:
1、proto增加c2ss方法;
讯享网service HelloService{ rpc hello(HelloRequest) returns (HelloResponse){} rpc c2ss(HelloRequest) returns (stream HelloResponse){} }
2、serviceImpl重写c2ss方法
@Override public void c2ss(HelloProto.HelloRequest request, StreamObserver<HelloProto.HelloResponse> responseObserver) {
//1、接收client的请求参数 String name = request.getName(); //2、完成业务的处理 System.out.println("name = "+ name); //3、根据业务处理的结果,提供响应。 for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
HelloProto.HelloResponse.Builder builder = HelloProto.HelloResponse.newBuilder(); builder.setResult("处理的结果: "+ i); HelloProto.HelloResponse helloResponse = builder.build(); responseObserver.onNext(helloResponse); //增加一个睡眠,模仿不同时刻 try {
Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e); } } responseObserver.onCompleted(); } 3、client发起响应
讯享网package com.lizy; import io.grpc.ManagedChannel; import io.grpc.ManagedChannelBuilder; import java.util.Iterator; public class GrpcClient2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //1. 创建通信的管道 ManagedChannel managedChannel = ManagedChannelBuilder.forAddress("localhost", 9000).usePlaintext().build(); //2. 获得代理对象 stub 存根。 try { HelloServiceGrpc.HelloServiceBlockingStub helloService = HelloServiceGrpc.newBlockingStub(managedChannel); //3.完成RPC调用 //3.1 准备参数 HelloProto.HelloRequest.Builder builder = HelloProto.HelloRequest.newBuilder(); builder.setName("李君临"); HelloProto.HelloRequest helloRequest = builder.build(); //3.2 进行功能rpc调用,获取响应的内容 Iterator<HelloProto.HelloResponse> helloResponseIterator = helloService.c2ss(helloRequest); while (helloResponseIterator.hasNext()){ HelloProto.HelloResponse helloResponse = helloResponseIterator.next(); String result = helloResponse.getResult(); System.out.println("result = "+result); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { managedChannel.shutdown(); } } }
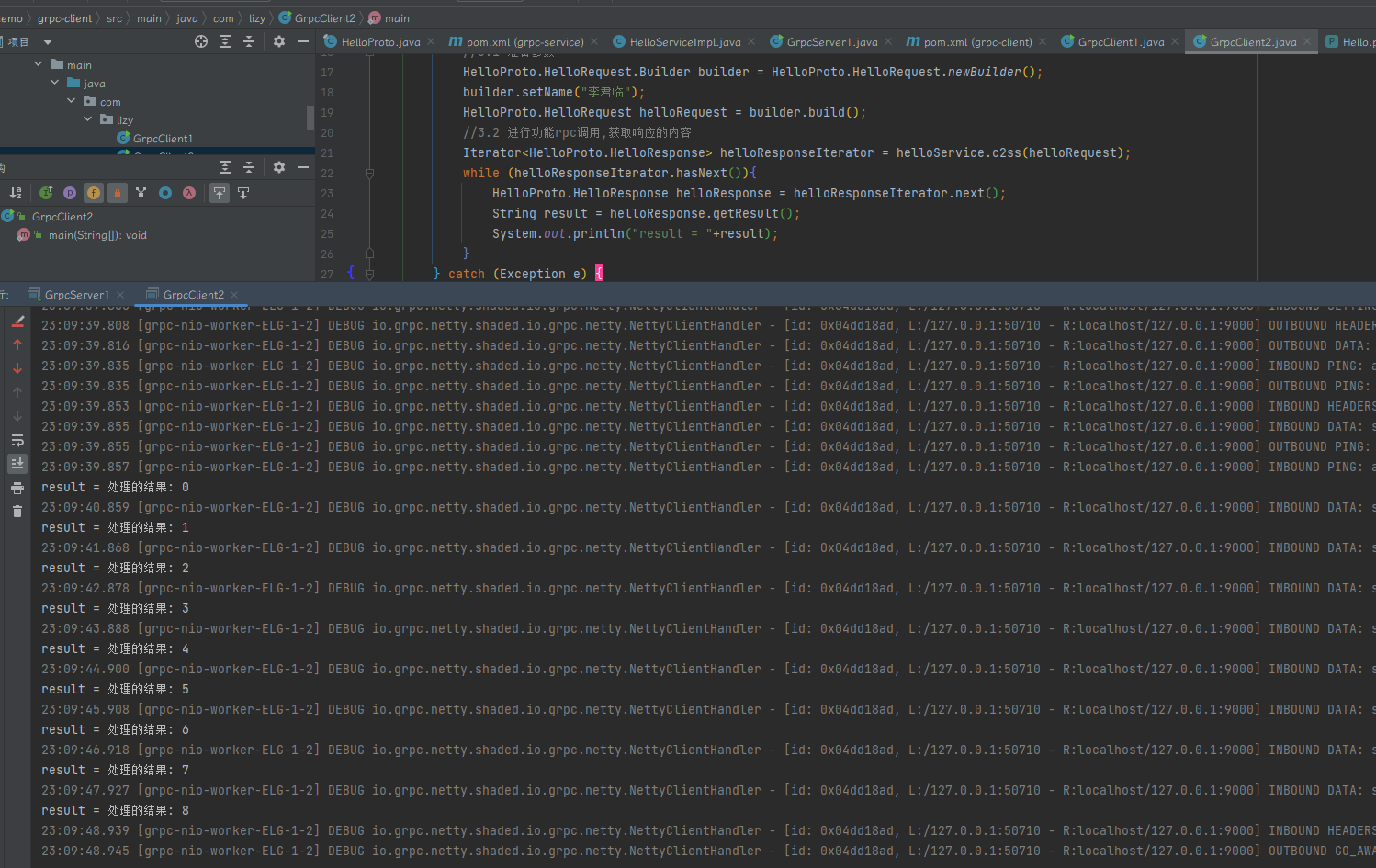
结果示例:
5、使用监听异步方式。
5.1、使用stub,而不是blockingstub
5.2、api,服务端代码不变
5.3、客户端代码如下
package com.lizy; import io.grpc.ManagedChannel; import io.grpc.ManagedChannelBuilder; import io.grpc.stub.StreamObserver; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class GrpcClient3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 创建通信的管道 ManagedChannel managedChannel = ManagedChannelBuilder.forAddress("localhost", 9000).usePlaintext().build(); //2. 获得代理对象 stub 存根。 try {
HelloServiceGrpc.HelloServiceStub helloServiceStub = HelloServiceGrpc.newStub(managedChannel); //3.完成RPC调用 //3.1 准备参数 HelloProto.HelloRequest.Builder builder = HelloProto.HelloRequest.newBuilder(); builder.setName("李君临"); HelloProto.HelloRequest helloRequest = builder.build(); //3.2 进行功能rpc调用,获取响应的内容 //StreamObserver 观察者模式 helloServiceStub.c2ss(helloRequest, new StreamObserver<HelloProto.HelloResponse>() {
@Override public void onNext(HelloProto.HelloResponse helloResponse) {
//服务端 响应了 一个消息后,需要立即处理话,把代码写在这里。 System.out.println("服务端每一次响应的消息 "+ helloResponse.getResult()); } @Override public void onError(Throwable throwable) {
} @Override public void onCompleted() {
//需要把服务端响应的所有数据拿到后,再进行业务处理。 //服务端 响应了 一个消息后,需要立即处理话,把代码写在这里。 System.out.println("服务端响应结束,后续可以根据需要,在这里统一处理服务端响应的内容"); } }); managedChannel.awaitTermination(12, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(); } finally {
managedChannel.shutdown(); } } } 5.4、注意问题
异步编程,因为没有阻塞,顺序执行了代码,直接shutdown了。
服务端想响应,都没办法响应。因为client已经关掉了通道。
5.4、客户端流式RPC
1、特点
客户端发送多个请求对象,服务只返回一个结果。
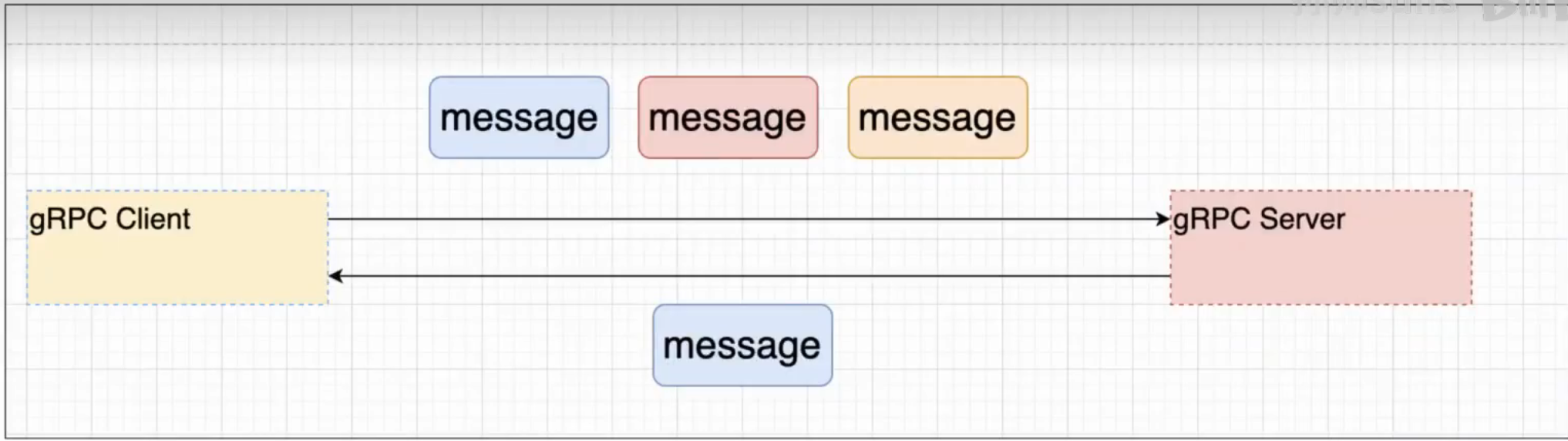
2、使用场景
IOT(互联网【传感器】)
这些终端给服务端发送数据。
传感器会经常性地给服务端发消息。
3、语法
proto
讯享网 rpc cs2s(stream HelloRequest) returns (HelloResponse){}
4、开发
4.1、api
rpc cs2s(stream HelloRequest) returns (HelloResponse){} 4.2、服务端开发
讯享网 @Override public StreamObserver<HelloProto.HelloRequest> cs2s(StreamObserver<HelloProto.HelloResponse> responseObserver) {
return new StreamObserver<HelloProto.HelloRequest>() {
@Override public void onNext(HelloProto.HelloRequest helloRequest) {
System.out.println("服务端收到一条消息:"+helloRequest.getName()); } @Override public void onError(Throwable throwable) {
} @Override public void onCompleted() {
System.out.println("全部接收完成"); HelloProto.HelloResponse.Builder builder = HelloProto.HelloResponse.newBuilder(); builder.setResult("this is result"); HelloProto.HelloResponse helloResponse = builder.build(); responseObserver.onNext(helloResponse); responseObserver.onCompleted(); } }; }
4.3、客户端开发
package com.lizy; import io.grpc.ManagedChannel; import io.grpc.ManagedChannelBuilder; import io.grpc.stub.StreamObserver; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class GrpcClient1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ManagedChannel managedChannel = ManagedChannelBuilder.forAddress("localhost", 9000).usePlaintext().build(); try {
HelloServiceGrpc.HelloServiceStub helloServiceStub = HelloServiceGrpc.newStub(managedChannel); StreamObserver<HelloProto.HelloRequest> requestStreamObserver = helloServiceStub.cs2s(new StreamObserver<HelloProto.HelloResponse>() {
@Override public void onNext(HelloProto.HelloResponse helloResponse) {
System.out.println("服务端 响应的数据内容为:" + helloResponse.getResult()); } @Override public void onError(Throwable throwable) {
} @Override public void onCompleted() {
System.out.println("服务端响应结束"); } }); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//对应的请求。每个请求。 //先定义返回,在定义请求。 HelloProto.HelloRequest.Builder builder = HelloProto.HelloRequest.newBuilder(); builder.setName("李"+i); HelloProto.HelloRequest request = builder.build(); requestStreamObserver.onNext(request); Thread.sleep(1000); } requestStreamObserver.onCompleted(); managedChannel.awaitTermination(12, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(); }finally {
managedChannel.shutdown(); } } } 如果在服务端处理next返回。
会提示
讯享网警告: Cancelling the stream with status Status{code=INTERNAL, description=Too many responses, cause=null}
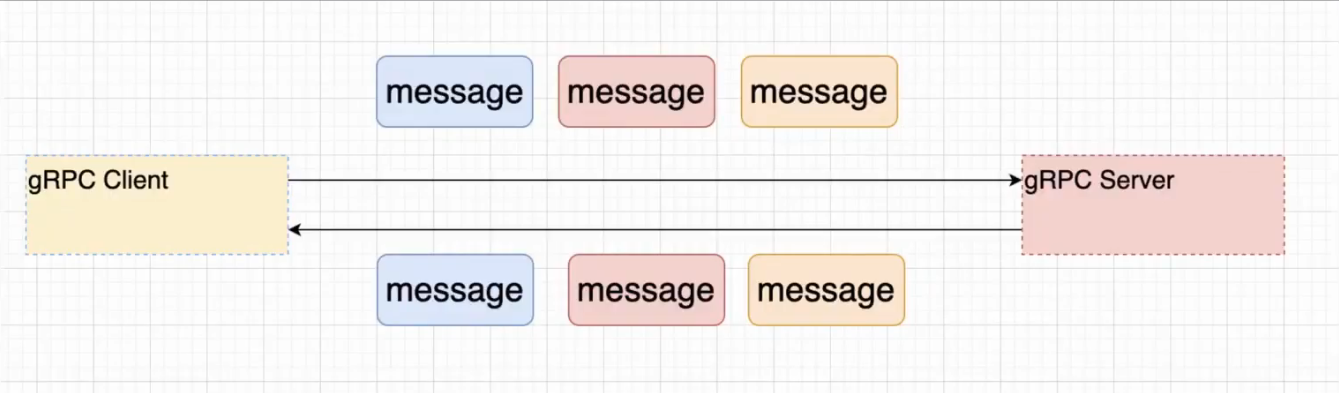
5.6、双向流式RPC
1、特点
客户端可以发送多个请求消息,服务端响应多个响应消息
2、应用场景
聊天室
3、语法
rpc cs2ss(stream HelloRequest) returns (stream HelloResponse){} 4、开发
4.1、api
讯享网rpc cs2ss(stream HelloRequest) returns (stream HelloResponse){}
4.2、server
@Override public StreamObserver<HelloProto.HelloRequest> cs2ss(StreamObserver<HelloProto.HelloResponse> responseObserver) { return new StreamObserver<HelloProto.HelloRequest>() { @Override public void onNext(HelloProto.HelloRequest helloRequest) { System.out.println("服务端收到一条消息:" + helloRequest.getName()); responseObserver.onNext(HelloProto.HelloResponse.newBuilder().setResult("response "+helloRequest.getName() + "result ").build()); } @Override public void onError(Throwable throwable) { } @Override public void onCompleted() { System.out.println("全部接收完成"); responseObserver.onCompleted(); } }; } 4.3、client
讯享网public class GrpcClient5 { public static void main(String[] args) { ManagedChannel managedChannel = ManagedChannelBuilder.forAddress("localhost", 9000).usePlaintext().build(); try { HelloServiceGrpc.HelloServiceStub helloServiceStub = HelloServiceGrpc.newStub(managedChannel); StreamObserver<HelloProto.HelloRequest> requestStreamObserver = helloServiceStub.cs2ss(new StreamObserver<HelloProto.HelloResponse>() { @Override public void onNext(HelloProto.HelloResponse helloResponse) { System.out.println("服务端 响应的数据内容为:" + helloResponse.getResult()); } @Override public void onError(Throwable throwable) { } @Override public void onCompleted() { System.out.println("服务端响应结束"); } }); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { //对应的请求。每个请求。 //先定义返回,在定义请求。 HelloProto.HelloRequest.Builder builder = HelloProto.HelloRequest.newBuilder(); builder.setName("李"+i); HelloProto.HelloRequest request = builder.build(); requestStreamObserver.onNext(request); Thread.sleep(1000); } requestStreamObserver.onCompleted(); managedChannel.awaitTermination(12, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { managedChannel.shutdown(); } } }
6、gRpc的代理方式
1. BlocingStub 阻塞 通信方式 2. Stub 异步 通过监听处理的 3. FutureStub 同步 / 异步 NettyFuture 1. FutureStub 只能应用一元RPC 6.1、futureStub代码
讯享网package com.lizy; import com.google.common.util.concurrent.FutureCallback; import com.google.common.util.concurrent.Futures; import com.google.common.util.concurrent.ListenableFuture; import io.grpc.ManagedChannel; import io.grpc.ManagedChannelBuilder; import io.grpc.stub.StreamObserver; import java.util.concurrent.Executor; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class GrpcClient6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ManagedChannel managedChannel = ManagedChannelBuilder.forAddress("localhost", 9000).usePlaintext().build(); try {
HelloServiceGrpc.HelloServiceFutureStub helloServiceFutureStub = HelloServiceGrpc.newFutureStub(managedChannel); ListenableFuture<HelloProto.HelloResponse> listenableFuture = helloServiceFutureStub.hello(HelloProto.HelloRequest.newBuilder().setName("李1").build()); //阻塞操作。 // HelloProto.HelloResponse helloResponse = listenableFuture.get(); // System.out.println(helloResponse.getResult()); //第一种异步操作 // listenableFuture.addListener(()->{
// System.out.println("异步的rpc响应回来了"); // }, Executors.newCachedThreadPool()); //第二种异步操作。 Futures.addCallback(listenableFuture, new FutureCallback<HelloProto.HelloResponse>() {
@Override public void onSuccess(HelloProto.HelloResponse result) {
System.out.println("异步的rpc响应回来了"+result.getResult()); } @Override public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
} }, Executors.newCachedThreadPool()); System.out.println("后续的操作..."); managedChannel.awaitTermination(12, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(); }finally {
managedChannel.shutdown(); } } }
7、gRpc与SpringBoot整合
7.1、gRpc与SpringBoot整合的思想
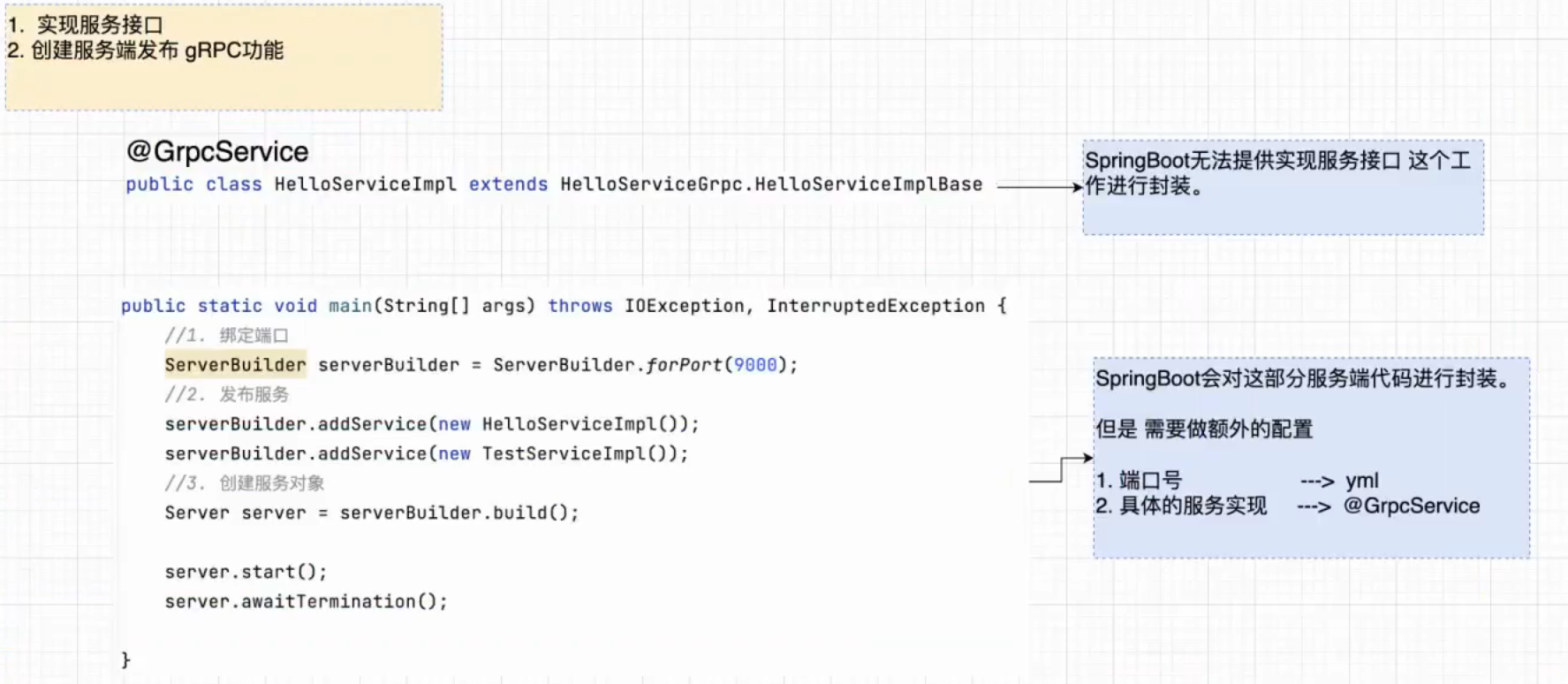
1. grp-server 2. grpc-client 7.2、解析
Springboot与gRpc整合过程中,对于服务端做了什么封装。
7.3、搭建开发环境
缺少依赖
cannot access com.google.protobuf.GeneratedMessageV3
解决方法:在pom中添加相关依赖
讯享网<dependency> <groupId>com.google.protobuf</groupId> <artifactId>protobuf-java</artifactId> <version>3.5.1</version> </dependency>
7.4、服务端开发
1、pom依赖
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.lizy</groupId> <artifactId>grpc-api</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <exclusions> <exclusion> <artifactId>error_prone_annotations</artifactId> <groupId>com.google.errorprone</groupId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>net.devh</groupId> <artifactId>grpc-server-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.14.0.RELEASE</version> <exclusions> <exclusion> <artifactId>error_prone_annotations</artifactId> <groupId>com.google.errorprone</groupId> </exclusion> <exclusion> <artifactId>protobuf-java</artifactId> <groupId>com.google.protobuf</groupId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> </dependencies> 2、yaml配置
讯享网# 核心配置的 就是gRpc的端口号 spring: application: name: boot-server # 取消 tomcat启动。netty服务可能也要这样做 main: web-application-type: none grpc: server: port: 9000
3、service配置
package com.liziyao.grpcbootsever.service; import com.lizy.HelloProto; import com.lizy.HelloServiceGrpc; import io.grpc.stub.StreamObserver; import net.devh.boot.grpc.server.service.GrpcService; @GrpcService public class HelloServiceImpl extends HelloServiceGrpc.HelloServiceImplBase {
@Override public void hello(HelloProto.HelloRequest request, StreamObserver<HelloProto.HelloResponse> responseObserver) {
String name = request.getName(); System.out.println("request 请求的name:" + name); responseObserver.onNext(HelloProto.HelloResponse.newBuilder().setResult("恭喜你返回成功").build()); responseObserver.onCompleted(); } } 7.5、客户端开发。
分析:
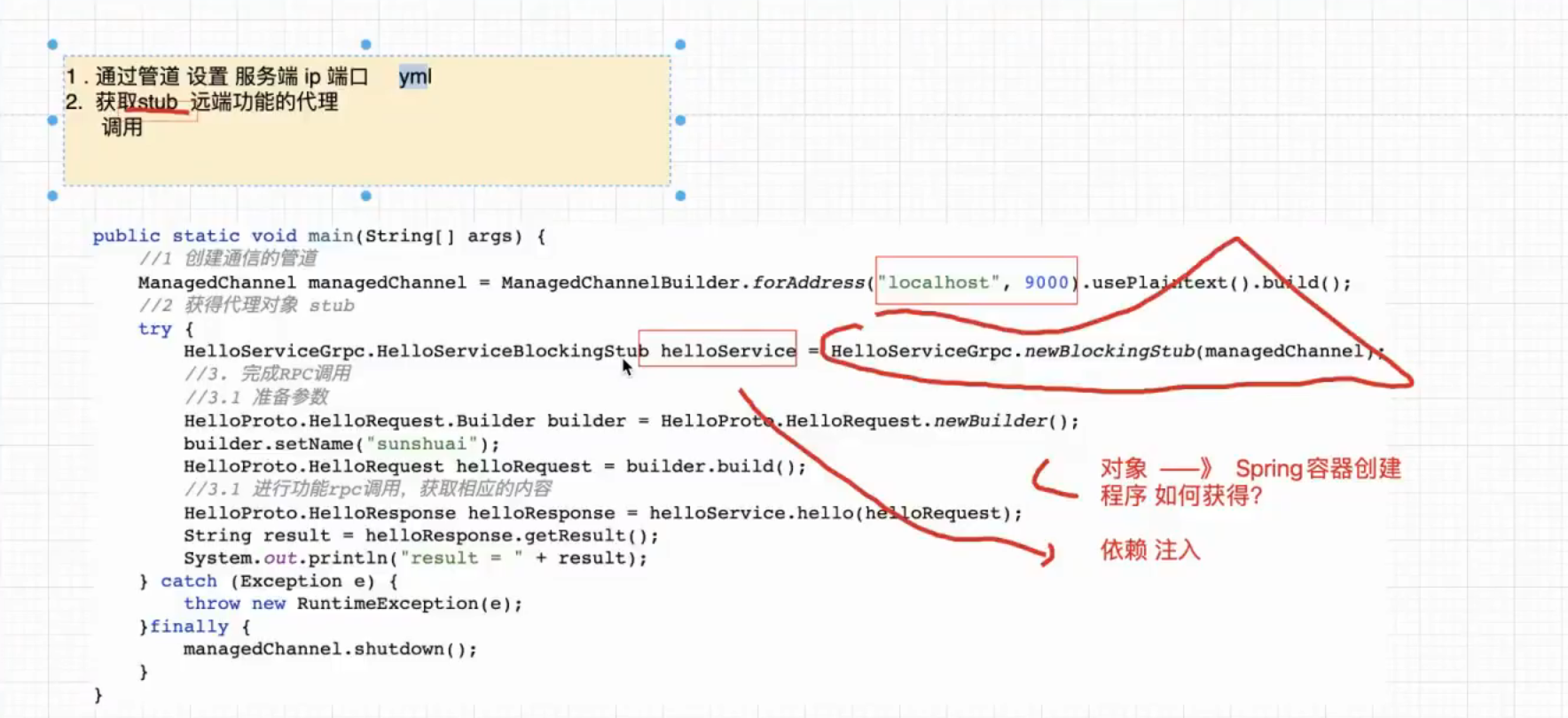
1、pom依赖。
讯享网 <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.lizy</groupId> <artifactId>grpc-api</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <exclusions> <exclusion> <artifactId>error_prone_annotations</artifactId> <groupId>com.google.errorprone</groupId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>net.devh</groupId> <artifactId>grpc-client-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.14.0.RELEASE</version> <exclusions> <exclusion> <artifactId>error_prone_annotations</artifactId> <groupId>com.google.errorprone</groupId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> </dependencies>
2、yaml配置
spring: application: name: boot-client grpc: client: grpc-server: address: 'static://127.0.0.1:9000' negotiation-type: plaintext 3、client配置
讯享网package com.liziyao.grpcbootclient.controller; import com.lizy.HelloProto; import com.lizy.HelloServiceGrpc; import net.devh.boot.grpc.client.inject.GrpcClient; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class HelloController {
@GrpcClient("grpc-server") private HelloServiceGrpc.HelloServiceBlockingStub stub; @GetMapping("hello") public String hello(String name){
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(name)) {
name = "扶摇直上"; } System.out.println("你好,进入了client方法"); HelloProto.HelloResponse response = stub.hello(HelloProto.HelloRequest.newBuilder().setName(name).build()); String result = response.getResult(); return result; } }
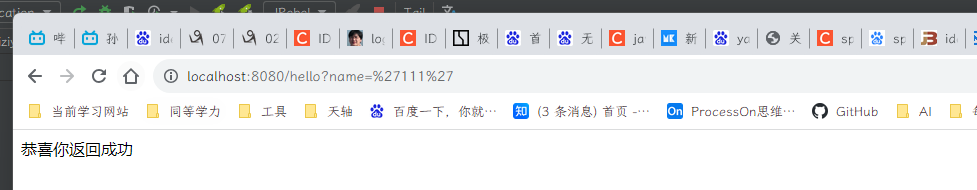
4、返回结果
8、高级用法
1. 拦截器 一元拦截器 2. Stream Tracer [监听器] 流拦截器 3. Retry Policy 客户端重试 4. NameResolver consule | ectd | nacos 5. 负载均衡 (pick-first,轮询) 6. grpc与微服务的整合 序列化(protobuf) Dubbo grpc Dubbo dubbo只做服务治理 grpc gateway grpc JWT grpc nacos2.0 grpc 替换 OpenFeign 7. grpc http2.x 多种通信方式。能和K8S 作整合。 
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容,请联系我们,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://51itzy.com/kjqy/43051.html