启发式算法
Heuristic Algorithm
Gary 2021.1.29
定义与简介
启发式算法 (Heuristic Algorithm) 是一种基于直观或经验的局部
人们常常把从大自然的运行规律或者面向具体问题的经验和规则中启发出来的方法称之为启发式算法. 现在的启发式算法也不是全部来自然的规律, 也有来自人类积累的工作经验.在可接受的花费 (指计算时间和空间) 下给出待解决组合化问题每一个实例的一个可行解, 该可行解与最优解的偏离程度不一定事先可以预计.启发式算法是一种技术, 该技术使得能在可接受的计算费用内去寻找尽可能好的解, 但不一定能保证所得解的可行性和最优性, 甚至在多数情况下, 无法描述所得解与最优解的近似程度.
几种经典的启发式算法
- 禁忌搜索 (Tabu Search): 它是对局部领域搜索的一种扩展,是一种全局逐步寻优算法, 是对人类智力过程的一种模拟.
- 模拟退火 (Simulated Annealing): 它是一种通过模拟物理退火过程搜索最优解的方法.
- 遗传算法 (Genetic Algorithms): 它是一种通过模拟自然进化过程搜索最优解的方法.
- 神经网络(Neural Networks): 它是一种模仿动物神经网络行为特征, 进行分布式并行信息处理的算法数学模型.
- 蚁群算法 (Ant Algorith): 它是一种模仿蚂蚁在寻找食物过程中发现路径的行为来寻找优化路径的机率型算法
经典问题
TSP 旅行商问题
经典问题: 旅行商问题
旅行商问题 (TSP): 假设有一个旅行商人要拜访 n 个城市, dij 表示两城市间距离. xij 为 0,1 变量, 表示拜访路径是否包函路径 dij.
限制: 每个城市必需且只能拜访一次,最后要回到原来出发的城市
目标: 路径的选择目标是要求所得路径,路程为所有路径之中的最小值
枚举尝试
以第一个城市为始终点, 计算任意一条路径 [1*,* i2*,* · · · , in, 1]的长度的基本运算为两两城市间距离求和, 基本操作次数为n. 路径的条数为 (n-1)!. 求和运算的总次数为(n -1)!*×n = n!.
时间复杂度太高
模拟退火和Metropolis原则
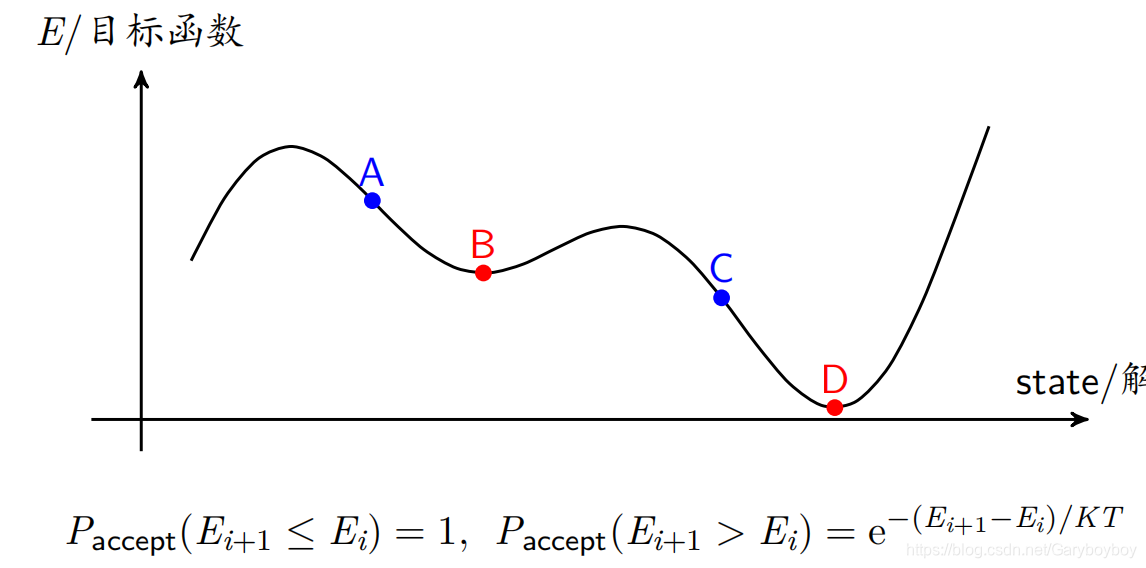
看到与贪心算法有些类似,但会以某个概率来接受另外一个解
算法步骤
| 设定初始解(通常是一个随机解或者挑选过后的解) |
|---|
| 目标函数 |
| 最优解 |
| 设定初始温度 |
| 扰动 |
| Metropolis采样过程 |
| 控制参数的下降 |
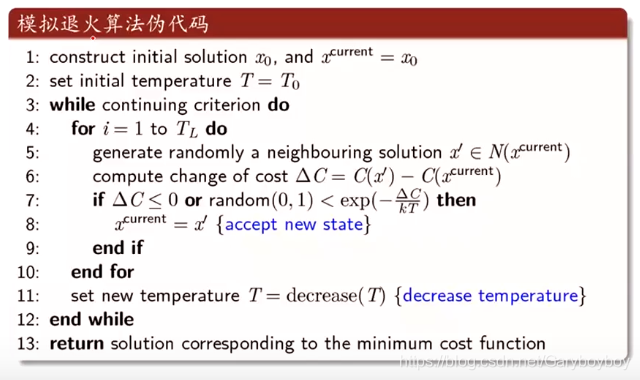
伪代码
算法设计要素
- 初始温度应该设置的尽可能的高, 以确保最终解不受初始解影响. 但过高又会增加计算时间.均匀抽样一组状态,以各状态目标值的方差为初温.
- 如果能确定邻解间目标函数 (COST 函数) 的最大差值, 就可以确定出初始温度 T0, 以使初始接受概率 P = e*−|∆C|max/T足够大. |∆C|*max 可由随机产生一组状态的最大目标值差来替代.
- 在正式开始退火算法前, 可进行一个升温过程确定初始温度:

- 逐渐增加温度, 直到所有的尝试尝试运动都被接受, 将此时的温度设置为初始温度.由经验给出, 或通过尝试找到较好的初始温度.
等温步数确定
等温步数也称 Metropolis 抽样稳定准则, 用于决定在各温度下产生候选解的数目. 通常取决于解空间和邻域的大小.
- 目标就是达到平衡,(目标函数均值稳定)
降温方式确定

花费函数(一般就是目标函数)
不宜过于复杂
理论上温度要降为 0 才终止退火算法. 但实际上温度较低时,尝试的接受概率就几乎为 0 了.
设置终止温度的阈值, 或设置外循环迭代次数.算法搜索到的最优值连续若干步保持不变.
模拟退火算法实例
已知中国 34 个省会城市 (包括直辖市) 的经纬度, 要求从北京出发, 游遍 34 个城市, 最后回到北京. 用模拟退火算法求最短路径.
初始解是什么?
给34个城市,标定一个1-34的顺序即可了
这里我们采用第三种降温函数
实现代码
% Initialize the route by generate a sequence of random route = randperm(numberofcities);% 随机排数据 % This is objective function, the total distance for the routes. previous_distance = totaldistance(route,dis); % This is a flag used to cool the current temperature after 100 iterations temperature_iterations = 1; % 用来控制降温的循环 % This is a flag used to plot the current route after 200 iterations plot_iterations = 1; % plot the current route plotroute(city, route, previous_distance, temperature); while 1.0 < temperature % generate randomly a neighbouring solution temp_route = perturb(route,'reverse'); % 扰动产生临解 % compute total distance of the temp_route current_distance = totaldistance(temp_route, dis); % compute change of distance diff = current_distance - previous_distance; % Metropolis Algorithm if (diff < 0) || (rand < exp(-diff/(temperature))) route = temp_route; %accept new route previous_distance = current_distance; % update iterations temperature_iterations = temperature_iterations + 1; plot_iterations = plot_iterations + 1; iterations = iterations + 1; end % reduce the temperature every 100 iterations if temperature_iterations >= 100 temperature = cooling_rate*temperature; temperature_iterations = 0; end % plot the current route every 200 iterations if plot_iterations >= 200 plotroute(city, route, previous_distance,temperature); plot_iterations = 0; end end 讯享网
扰动函数
讯享网function route = perturb(route_old, method) % PERTURB % route = PERTURB(route_old, method) generate randomly a neighbouring route by % perturb old route. perturb methods: % ___________ ___________ % 1. reverse: [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] -> [1 2 8 7 6 5 4 3 9] % _ _ _ _ % 2. swap: [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] -> [1 2 8 4 5 6 7 3 9] route = route_old; numbercities = length(route); city1 = ceil(numbercities*rand); city2 = ceil(numbercities*rand); %随机挑选两个城市 switch method case 'reverse' citymin = min(city1,city2); citymax = max(city1,city2); route(citymin:citymax) = route(citymax:-1:citymin); case 'swap' route([city1, city2]) = route([city2, city1]); end
路径计算长度函数
function dis = distancematrix(city) % DISTANCEMATRIX % dis = DISTANCEMATRIX(city) return the distance matrix, dis(i,j) is the % distance between city_i and city_j numberofcities = length(city); R = 6378.137; % The radius of the Earth (地球的半径) for i = 1:numberofcities for j = i+1:numberofcities dis(i,j) = distance(city(i).lat, city(i).long, ... city(j).lat, city(j).long, R); dis(j,i) = dis(i,j); end end function d = distance(lat1, long1, lat2, long2, R) % DISTANCE % d = DISTANCE(lat1, long1, lat2, long2, R) compute distance between points % on sphere with radians R. % % Latitude/Longitude Distance Calculation: % http://www.mathforum.com/library/drmath/view/51711.html
y1 = lat1/180*pi; x1 = long1/180*pi; y2 = lat2/180*pi; x2 = long2/180*pi; dy = y1-y2; dx = x1-x2; d = 2*R*asin(sqrt(sin(dy/2)^2+sin(dx/2)^2*cos(y1)*cos(y2))); function d = totaldistance(route, dis) % TOTALDISTANCE % d = TOTALDISTANCE(route, dis) calculate total distance of a route with % the distance matrix dis. d = dis(route(end),route(1)); % closed path for k = 1:length(route)-1 i = route(k); j = route(k+1); d = d + dis(i,j); end 遗传算法
- 基因 (Gene)
染色体上的一个单元, 解中的一个参数.
- 染色体 (Chromosome)
由一组基因构成, 问题可能的一个解.
- 种群 (Population)
由一系列染色体组成的一个集合.
算法框架与伪代码

编码
二进制编码,格雷码…
适应度函数
适应度函数也称评价函数, 是根据目标函数确定的用于区分群体中个体好坏的标准. 适应度函数值的大小是对个体的优胜劣汰的依据.
- 通常适应度函数可以由目标函数直接或间接改造得到. 比如,目标函数, 或目标函数的倒数/相反数经常被直接用作适应度函数.
- 一般情况下==适应度是非负的, 并且总是希望适应度越大越好==(适应度值与解的优劣成反比例).
- 比较好的适应度函数应: 单值, 连续, 非负, 最大化.适应度函数不应过于复杂, 越简单越好, 以便于计算机的快速计算.
选择方式
- 轮盘赌: 又称比例选择算子, 个体 i 被选中的概率pi 与其适应度成正比.
pi = fi/∑(Nj*=1 ) fj
- 两两竞争: 从父代中随机地选取两个个体, 比较适应值, 保存优秀个体, 淘汰较差的个体.
- 排序选择: 根据各个体的适应度大小进行排序, 然后基于所排序号进行选择.
TSP问题遗传算法求解
适应度函数:1/总距离
- 如何交叉运算设计?
- 如何变异运算设计?
讯享网popSize = 100; % population size max_generation = 1000; % number of generation probmutation = 0.16; % probability of mutation % Initialize random number generator with "seed". rand('seed',103); % Initialize the pop: start from random routes pop = zeros(popSize,numberofcities); for i=1:popSize pop(i,:)=randperm(numberofcities); % 初始化了100组解 end for generation = 1:max_generation % generations loop % evaluate: compute fitness(1/totaldistance) for each individuals in pop popDist = totaldistance(pop,dis); fitness = 1./popDist; % find the best route & distance [mindist, bestID] = min(popDist); bestPop = pop(bestID, :); % best route % update best route on figure: if mod(generation,10)==0 plotroute(city, bestPop, mindist, generation) end % select (competition / roulette) pop = select(pop, fitness, popSize,'competition'); % crossover pop = crossover(pop); % mutation pop = mutation(pop, probmutation); % save elitism(best path) and put it to next generation without changes pop = [bestPop; pop]; end % return the best route [mindist, bestID]=min(popDist); bestPop = pop(bestID, :); % plot the final solution plotroute(city, bestPop, mindist, generation);
选择设计
function popselected = select(pop, fitness, nselected, method) % SELECT % popselected = SELECT(pop, fitness, nselected, method) select the fittest % individuals to survive to the next generation. % popSize = size(pop,1); switch method case 'roulette' p=fitness/sum(fitness); % probabilities of select cump=cumsum(p); % cumulative sum of probabilities I = interp1([0 cump],1:(popSize+1),rand(1,nselected),'linear'); % random numbers from 1:nselected according probabilities I = floor(I); case 'competition' % randomly generated two sets of population i1 = ceil( popSize*rand(1,nselected) ); i2 = ceil( popSize*rand(1,nselected) ); % compare the fitness and select the fitter I = i1.*( fitness(i1)>=fitness(i2) ) + ... i2.*( fitness(i1)< fitness(i2) ); end popselected=pop(I,:); 交叉设计
讯享网function children = crossover(parents) % CROSSOVER % children = CROSSOVER(parents) Replicate the mating process by crossing % over randomly selected parents. % % Mapped Crossover (PMX) example: % _ _ _ % [1 2 3|4 5 6 7|8 9] |-> [4 2 3|1 5 6 7|8 9] |-> [4 2 3|1 8 6 7|5 9] % [3 5 4|1 8 7 6|9 2] | [3 5 1|4 8 7 6|9 2] | [3 8 1|4 5 7 6|9 2] % | | | | | % V | V | | % [* 2 3|1 5 6 7|8 9] _| [4 2 3|1 8 6 7|* 9] _| V % [3 5 *|4 8 7 6|9 2] [3 * 1|4 5 7 6|9 2] ... ... ... % [popSize, numberofcities] = size(parents); children = parents; % childrens for i = 1:2:popSize % pairs counting parent1 = parents(i+0,:); child1 = parent1; parent2 = parents(i+1,:); child2 = parent2; % chose two random points of cross-section InsertPoints = sort(ceil(numberofcities*rand(1,2))); for j = InsertPoints(1):InsertPoints(2) if parent1(j)~=parent2(j) child1(child1==parent2(j)) = child1(j); child1(j) = parent2(j); child2(child2==parent1(j)) = child2(j); child2(j) = parent1(j); end end % two childrens: children(i+0,:)=child1; children(i+1,:)=child2; end
变异设计
以固定的概率变异
function children = mutation(parents, probmutation) % MUTATION % children = MUTATION(parents, probmutation) Replicate mutation in the % population by selecting an individual with probability probmutation % % swap: _ _ slide: _ _________ flip: ----------> % [1 2|3 4 5 6 7 8|9] [1 2|3 4 5 6 7 8|9] [1 2|3 4 5 6 7 8|9] % _________ _ <---------- % [1 2|8 4 5 6 7 3|9] [1 2|4 5 6 7 8 3|9] [1 2|8 7 6 5 4 3|9] % [popSize, numberofcities] = size(parents); children = parents; for k=1:popSize if rand < probmutation InsertPoints = ceil(numberofcities*rand(1,2)); I = min(InsertPoints); J = max(InsertPoints); switch ceil(rand*6) case 1 % swap children(k,[I J]) = parents(k,[J I]); case 2 % slide children(k,[I:J]) = parents(k,[I+1:J I]); otherwise % flip children(k,[I:J]) = parents(k,[J:-1:I]); end end end 具体完整代码,请见数学建模



版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容,请联系我们,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://51itzy.com/kjqy/105847.html