参考:2021-06-23 基于AprilTag的位姿估计,原理,完整代码(相机坐标系、世界坐标系) - 简书
Apriltag使用之二:方位估计(定位)_arczee的博客-CSDN博客_apriltag位姿估计
https://www.cnblogs.com/brt2/p/13547075.html
根据Apriltag进行角度和距离检测_卓晴的博客-CSDN博客_apriltag
1.AprilTag概述
AprilTag是一种视觉基准系统,类似的视觉基准标签还有:ArUco、ARTag、TopoTag等。而AprilTag因其对旋转、光照、模糊具有良好的鲁棒性,因此被广泛应用于目标跟踪、室内定位、增强现实等领域。本文主要展示使用AprilTag标签,分别获取AprilTag标签在相机坐标系下和世界坐标系下位置。
1.1 相机内参
相机内参存放于K中,例:K = (cv::Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 471.33715, 0.0, 437.19435, 0.0, 472.0701, 275.1862, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);则横向焦距fx=471.33715,竖向焦距为437.19435,偏移量为472和275.

生成AprilTag不同家族标签图像教程
2.AprilTag 相关资料
AprilTag论文三部曲:
- AprilTag: A robust and flexible visual fiducial system. --2011
- AprilTag 2: Efficient and robust fiducial detection. --2016
- Flexible Layouts for Fiducial Tags. --2019(AprilTag3)
一些应用AprilTag的论文:
- UAV Autonomous Landing Technology Based on AprilTags Vision Positioning Algorithm.
- Pose Estimation for Multicopters Based on Monocular Vision and AprilTag.
- Image Digital Zoom Based Single Target Apriltag Recognition Algorithm in Large Scale Changes on the Distance.
上述资料打包下载地址:https://cloud.189.cn/web/share?code=JRJRJbNfe2ay(访问码:7l96)
AprilTag论文源码地址:https://github.com/AprilRobotics/apriltag
官网:https://april.eecs.umich.edu/software/apriltag.html
git仓库地址:https://github.com/AprilRobotics/apriltag
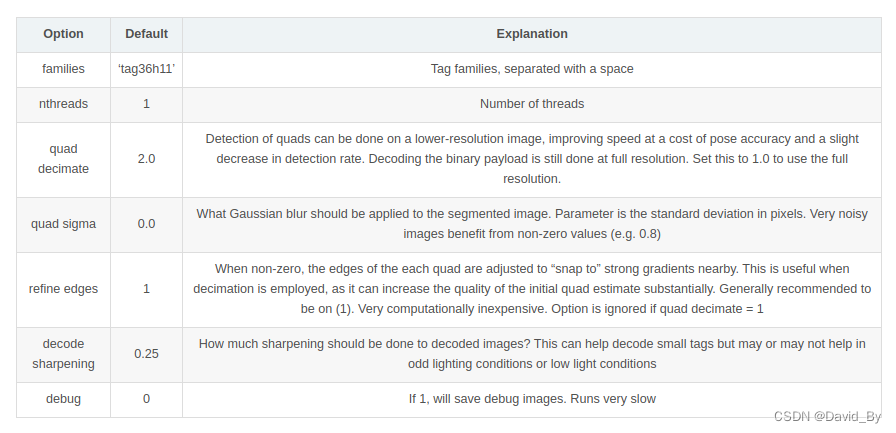
2.1 参数配置
td_ = apriltag_detector_create();
tf_ = tag36h11_create();//tag种类
apriltag_detector_add_family_bits(td_, tf_, 3);
td_->quad_decimate = 1; // Decimate input image by factor //降低图片分辨率,经实验该参数可大幅提升检测时间且不影响检测结果
td_->quad_sigma = 0; // No blur //高斯降噪,如果噪声较大的图片,可使用该参数
td_->nthreads = 4; // 2 treads provided //使用几个线程来运行
td_->debug = 0; // No debuging output
td_->refine_edges = 1;
info_.tagsize = APRILTAG_DETECTED_SIZE;//TAG大小
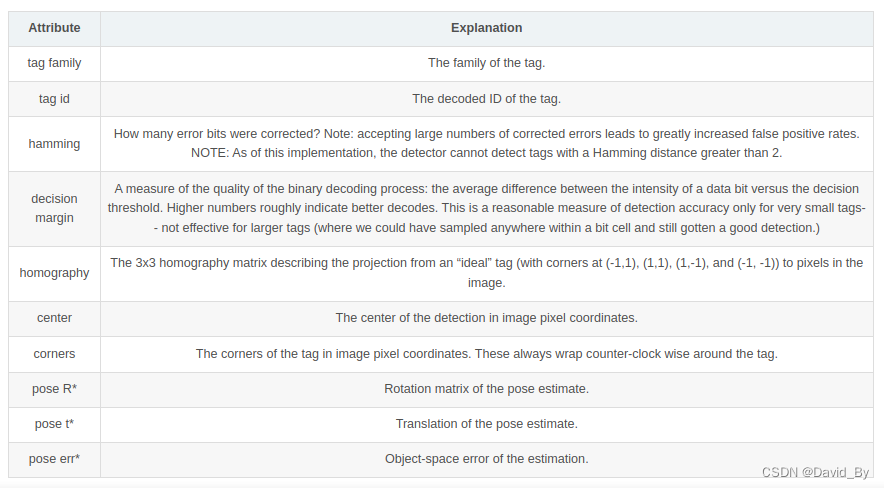
2.2检测结果含义
3.AprilTag 原理
检测标签

0.高斯滤波 (解决边缘遮挡)

1.前端检测二维码(像素梯度,直线拟合,查找矩形,家族对比)
实现原理
自适应阈值
将输入图像(a)灰度化处理为灰度图(b)。采用自适应阈值方法,自适应阈值的主要思想就是在像素领域内寻找一个合理的阈值进行分割,选取灰度均值和中值都是常见的手法。作者先将图像划分为4x4像素的图块,求出每个图块的灰度最大值和最小值,然后对所有图块计算的最大最小灰度值进行一个3邻域最大最小滤波处理,将滤波后的最大最小均值(max+min)/2作为分块区域的阈值,为每个像素分配白色或黑色的值形成二值图。分块的目的主要是增加鲁棒性,区域的特征总比单一像素的更加稳定,减少随机噪声的干扰,同时提升计算效率。


1.检测是否使用模糊参数
2.apriltag_quad_thresh检测矩形->step 1. threshold the image, creating the edge image.->seg img
zarray_t *apriltag_quad_thresh(apriltag_detector_t *td, image_u8_t *im) { // step 1. threshold the image, creating the edge image. int w = im->width, h = im->height; image_u8_t *threshim = threshold(td, im); // 线段检测 int ts = threshim->stride; if (td->debug) image_u8_write_pnm(threshim, "debug_threshold.pnm"); // step 2. find connected components. unionfind_t *uf = connected_components(td, threshim, w, h, ts); // make segmentation image.//分割图片 zarray_t *clusters = gradient_clusters(td, threshim, w, h, ts, uf); // step 3. process each connected component.深度优先搜索(深度为四的DFS确定四边形) zarray_t *quads = fit_quads(td, w, h, clusters, im); }解码:8×8判断黑白,如果为黑rcode<<1

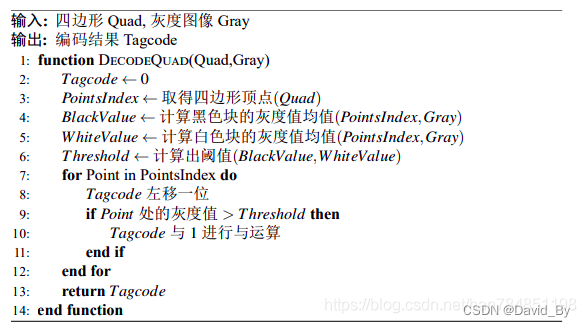

在确定的四边形中明确点阵坐标,在灰度图像中提取点阵的最外围一圈的像素的平均值Value1,再提取点阵次外外围一圈的像素的平均值Value2,根据AprilTag本身的二维码库的设计,四边形最外一层的虽有点的灰度值都是黑色的,而此外层的灰度值是黑色与白色混合,因此在同一光照环境下,Value1和Value2有明显的阈值分界线,确定阈值为Value1与Value2的均值,重新遍历整个点阵所有点坐标的像素值高于阈值的部分编码为0,低于阈值的部分编码为1,见图\ref{图片点阵}。如此以来,从第一行开始进行编码,直至整个点阵被编码完成,将编码排列起来会得到一串二进制码,该二进制码的长度由具体的编码方式决定(分为36,25,16三种),每个四边形都能得到一串二进制码,该码表示该状态下二维码的编码,错误的四边形往往会生成错误的编码,错误编码无法在阈值范围内匹配到相应的ID,故可以轻松的排除错误编码的四边形,对得到的四边形进行编码并进行匹配校验是重要的一个过程。
进一步确定编码是否可靠,要与已知的编码库进行匹配,由于观察到的编码存在旋转的情况,所以应先将得到的编码进行三次90°旋转共得到四个方向上的编码,再逐一与编码库进行比较,求解编码之间的汉明距离(Hamming Distance,汉明距离是表示两个二进制编码之间的相似程度的一种距离,汉明距离是两个长二进制串之间位数不相同的个数。当观察编码与已知库里的某一编码的汉明距离小于给定的阈值时(一般为2),就确定该观察编码的ID为与之匹配的编码库里的ID,并记录下该汉明距离,若编码库并没有一个与之匹配就确定该观察编码有误,则舍弃该编码对应的四边形。
内部遮挡优化:Step 2. Decode tags from each quad.
apriltag_detector_detect->quad_decode->quad_decode_task->quad_decode->quick_decode_codeword:设置偏差为5,能解决内部遮挡无法解决边界遮挡
讯享网 // qd might be null if detector_add_family_bits() failed for (int ridx = 0; qd != NULL && ridx < 4; ridx++) { for (int bucket = rcode % qd->nentries; qd->entries[bucket].rcode != UINT64_MAX; bucket = (bucket + 1) % qd->nentries) { if (abs(qd->entries[bucket].rcode - rcode) < 5) { *entry = qd->entries[bucket]; entry->rotation = ridx; return; } } rcode = rotate90(rcode, tf->nbits); }
经过上述的筛选与验证,至此观察编码的ID以及编码的旋转已经可以确定,便可计算该二维码的其他参数,包括二维码相对于原二维码的旋转方位,观察二维码与匹配二维码的相似程度,其中主要为二维码的单线性变换矩阵(Homography Matrix)},在计算机领域中的针孔相机模型下,同一个张图形在不同空间内都有相关性,单线性变换就是将这个图片在该空间下映射至另一个与之对应的空间下,单线性变化矩阵就是这种映射矩阵且可分解出寻转矩阵与平移矩阵,根据上一个步骤求出的四个顶点的坐标即可求出相对于原始坐标的单线性变换矩阵,利用单线性变换矩阵结合多相机的信息,可以得到二维码的相关姿势信息。分解该矩阵就可求出旋转变换向量rvec以及平移变换向量tvec,对于得到的旋转向量,可以根据该向量求得二维码的正确姿势。
2.后端正交迭代法计算求解RT


matlab验证:位姿测量 | 正交迭代(OI)算法的原理及其MATLAB实现_正交迭代算法_lovetaozibaby的博客-CSDN博客
程序源码:
double orthogonal_iteration(matd_t v, matd_t p, matd_t t, matd_t R, int n_points, int n_steps) { /*对特征点归一化处理,求解P矩阵, P值为固定值不发生变化*/ matd_t *p_mean = matd_create(3, 1); for (int i = 0; i < n_points; i++) { matd_add_inplace(p_mean, p[i]); // 将p矩阵赋值给p_mean } matd_scale_inplace(p_mean, 1.0 / n_points); // P_mean与1/n相乘 matd_t p_res = malloc(sizeof(matd_t *) * n_points); for (int i = 0; i < n_points; i++) { p_res[i] = matd_op("M-M", p[i], p_mean); // 相减p-p_mean } /*求解当前帧的最优位置参数T的固定部分*/ matd_t F = malloc(sizeof(matd_t *) * n_points); matd_t *avg_F = matd_create(3, 3); for (int i = 0; i < n_points; i++) { F[i] = calculate_F(v[i]); // Fi 表示沿实现方向的投影矩阵 matd_add_inplace(avg_F, F[i]); } matd_scale_inplace(avg_F, 1.0 / n_points); // // 求解M矩阵 // Compute M1_inv. matd_t *I3 = matd_identity(3); // 单位阵 matd_t *M1 = matd_subtract(I3, avg_F); // 单位阵-F matd_t *M1_inv = matd_inverse(M1); // M1的逆矩阵(I-1/n(Vi))(-1) matd_destroy(avg_F); matd_destroy(M1); double prev_error = HUGE_VAL; // 无穷 double the = 37.0 / 180.0 * 3.14; double hmin = 0.1; double hmax = 0.4; // Iterate. for (int i = 0; i < n_steps; i++) // 迭代次数500 { // Calculate translation.求解最优参数T matd_t *M2 = matd_create(3, 1); for (int j = 0; j < n_points; j++) { matd_t *M2_update = matd_op("(M - M)*M*M", F[j], I3, *R, p[j]); //(V-I3)*R*P matd_add_inplace(M2, M2_update); // M2为四个点得累加值 matd_destroy(M2_update); } matd_scale_inplace(M2, 1.0 / n_points); // M2*(1/n) matd_destroy(*t); *t = matd_multiply(M1_inv, M2); // 求解当前帧的最优位置参数T,t为最优参数 // printf("z %f*\n", matd_get(*t, 0, 1)); /*if (matd_get(*t, 0, 1) < -0.9) // z方向限制 高度 matd_put(*t, 0, 1, -0.9); else if (matd_get(*t, 0, 1) > 0.2) matd_put(*t, 0, 1, 0.2); */ /*if (matd_get(*t, 0, 1) < -tan(the) * (matd_get(*t, 0, 2) - hmin / sin(the))) { matd_put(*t, 0, 1, -tan(the) * (matd_get(*t, 0, 2) - hmin / sin(the))); } else if (matd_get(*t, 0, 1) > -tan(the) * (matd_get(*t, 0, 2) - hmax / sin(the))) { matd_put(*t, 0, 1, -tan(the) * (matd_get(*t, 0, 2) - hmax / sin(the))); }*/ /*if (matd_get(*t, 0, 0) < -1.0) // x方向限制 matd_put(*t, 0, 0, -0.0); else if (matd_get(*t, 0, 0) > 1.0) matd_put(*t, 0, 0, 0.0);*/ matd_destroy(M2); // Calculate rotation.将q归一化处理 matd_t q = malloc(sizeof(matd_t *) * n_points); matd_t *q_mean = matd_create(3, 1); for (int j = 0; j < n_points; j++) { q[j] = matd_op("M*(M*M+M)", F[j], *R, p[j], *t); // 求解qi=V(R*P+T)=(R*P+t) matd_add_inplace(q_mean, q[j]); // v*q_mean=v*Q平均 } matd_scale_inplace(q_mean, 1.0 / n_points); matd_t *M3 = matd_create(3, 3); for (int j = 0; j < n_points; j++) { matd_t *M3_update = matd_op("(M-M)*M'", q[j], q_mean, p_res[j]); // M=P'Qi'(Rk) V*Qi'=V*(q-q_mean) matd_add_inplace(M3, M3_update); matd_destroy(M3_update); } matd_svd_t M3_svd = matd_svd(M3); // 奇异值分解 matd_destroy(M3); matd_destroy(*R); *R = matd_op("M*M'", M3_svd.U, M3_svd.V); // R=VU(T) /*(1)行列式的意义 单位面积/单位体积缩放或者拉升的比例 线性变换对空间压缩或者拉升的比例 线性变换会对空间进行挤压或者拉伸,我们通过追踪空间基向量的变换,来查看单位面积(二维)/单位体积(三维)的面积或者体积缩放比例,而这个缩放比例,对应的就是行列式的值。 二维空间中行列式的值表示平行四边形的面积, 三维空间中行列式的值表示平行六面体的体积*/ double R_det = matd_det(*R); // 行列式小于0,这样的结果就是空间取向发生了变换,即将整个空间翻转了一遍 if (R_det < 0) { matd_put(*R, 0, 2, -matd_get(*R, 0, 2)); // 行列式值进行翻转 matd_put(*R, 1, 2, -matd_get(*R, 1, 2)); matd_put(*R, 2, 2, -matd_get(*R, 2, 2)); } matd_destroy(M3_svd.U); matd_destroy(M3_svd.S); matd_destroy(M3_svd.V); matd_destroy(q_mean); for (int j = 0; j < n_points; j++) { matd_destroy(q[j]); } double error = 0; for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) { matd_t *err_vec = matd_op("(M-M)(MM+M)", I3, F[j], *R, p[j], *t); // 误差函数=(I-F)(R*P+t),误差项 F=V error += matd_to_double(matd_op("M'M", err_vec, err_vec)); // err^2 从几何角度看,点积是两个向量的长度与它们夹角余弦的积 matd_destroy(err_vec); } prev_error = error; free(q); } matd_destroy(I3); matd_destroy(M1_inv); for (int i = 0; i < n_points; i++) { matd_destroy(p_res[i]); matd_destroy(F[i]); } free(p_res); free(F); matd_destroy(p_mean); return prev_error; }- Apriltag中计算的Homography
配置参数,调用模型检测,在进行apriltag码检测时,如果检测到会一并计算出图像上apriltag码四个角点对应的homography矩阵,这个homography将这些点映射到到标准的(-1,1),(1,1),(1,-1),(-1,-1)顶点。 - 单应性变换与外参估计,通过给定相机的内参K,就可以利用homography对相机相对于apriltag码的方位进行估计。下面通过分析Apriltag的源码,阐述一下利用homography估计相机方位的方法。

以TAG右上角点坐标为例,在TAG坐标系中,X=Y,则:




- 位置与角度计算


- 距离估计:根据投影关系,可以根据检测到的Apriltag的对角线的长度与摄像头的焦距的几何关系,可以获得物体距离摄像头的距离。

3.解算位姿及优化
现在我们已知了由世界坐标系至相机坐标系的旋转矩阵和平移矩阵,现在可以根据这两个矩阵,估计相机在世界坐标系下的位置和相机坐标系下标签的位置。
1. 相机在世界坐标系下的位置
根据相机坐标系与世界坐标系之间的关系可知:
因为相机在相机坐标系下的坐标为,因此可得:
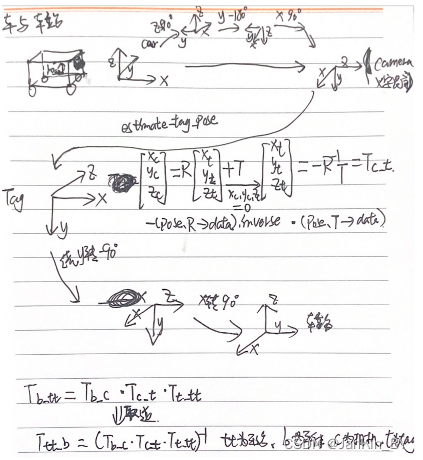
4.为ApriTag论文源码
讯享网/*调试经验: 1.相机位姿的精度主要取决于tag四个角点的检测像素精度。根据以前测试经验,存在角点误检,导致位姿误差大。主要有两种情况: 一、运动(特别是转弯)过程中照片有点模糊 二、相机与tag存在较大的倾角(30度以外误差比较大) 三、距离越远,误差越大,2m以外谨慎使用。 可能还要其他情况导致误检。 另外相机的内参也会影响计算的位姿,一定要标定好相机内参(重投影误差<0.15),做好畸变校正。 故需要加入严格的判断,最好让相机是正对mark。 */ #include "tag_station_detection.hpp" CREATE_LOGex(TagStationDetectionTask); TagStationDetection::TagStationDetection() { td_ = apriltag_detector_create(); tf_ = tag36h11_create(); // apriltag_detector_add_family(td_, tf_); apriltag_detector_add_family_bits(td_, tf_, 3); td_->quad_decimate = 1.0; // Decimate input image by factor //降低图片分辨率,经实验该参数可大幅提升检测时间且不影响检测结果 td_->quad_sigma = 0; // No blur //高斯降噪,如果噪声较大的图片,可使用该参数 td_->nthreads = 2; // 2 treads provided //使用几个线程来运行 td_->debug = 0; // No debuging output td_->refine_edges = 1; info_.tagsize = APRILTAG_DETECTED_SIZE; cv::Mat K, D; if (HIGH_RESOLUTION) { K = (cv::Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 471.33715, 0.0, 437.19435, 0.0, 472.0701, 275.1862, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); D = (cv::Mat_<double>(5, 1) << -0., 0.060122, -0.000640, 0.001716, 0.000000); } else { // K = (cv::Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 343.029387, 0.0, 320., 0.0, 342., 200., 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // D = (cv::Mat_<double>(5, 1) << -0., 0.095372, -0.003143, -0.001278, 0.000000); K = (cv::Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 319.88, 0.0, 315.43, 0.0, 319.27, 199.022, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); D = (cv::Mat_<double>(5, 1) << -0.08819, 0.079753, -0.00, 0.00021735, 0.0); } cv::Size img_size(img_width_, img_height_); initUndistortRectifyMap(K, D, cv::Mat(), K, img_size, CV_16SC2, map1_, map2_);//图片去畸变 cv::Mat new_camera_matric = cv::getOptimalNewCameraMatrix(K, D, img_size, 1); cv::initUndistortRectifyMap(K, D, cv::Mat(), new_camera_matric, img_size, CV_16SC2, map1_, map2_); if (TAG_IMG_UNDISTORT) K = new_camera_matric; info_.fx = K.at<double>(0, 0); info_.fy = K.at<double>(1, 1); info_.cx = K.at<double>(0, 2); info_.cy = K.at<double>(1, 2); Eigen::Vector3d ea_cam_slope(0, 0, -37.0 / 180 * CV_PI); // Eigen::Vector3d ea_cam_slope(0, 0, 0.0 / 180 * CV_PI); //绕不同轴进行旋转 旋转相机 ZYX 相机变换 rot_cam_slope_ = Eigen::AngleAxisd(ea_cam_slope[0], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ()) * //默认为单位矩阵,绕z轴旋转0度,结果为单位矩阵 Eigen::AngleAxisd(ea_cam_slope[1], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY()) * //绕y轴旋转0弧度,结果不变 Eigen::AngleAxisd(ea_cam_slope[2], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX()); //绕x轴旋转-37/180×pi弧度 绕x轴右乘 //绕z轴旋转90度,绕y轴旋转-180 绕x轴旋转90,在z方向向上平移 0.1m Eigen::Quaterniond quat_b_c(0.5, -0.5, 0.5, -0.5); //w,x,y,z,四元数4×1 90 -180 90 -0.5i+0.5j-0.5k+0.5 Eigen::Matrix3d rot_mat_b_c; rot_mat_b_c = quat_b_c.toRotationMatrix();//四元数转矩阵 Eigen::Translation3d trans_b_c(0.0, 0.0, 0.1); Tb_c_ = trans_b_c * rot_mat_b_c; //绕z轴旋转0度,绕y轴旋转-90度,绕x轴旋转90度,平移0 Eigen::Quaterniond quat_t_tt(0.5, 0.5, -0.5, 0.5); // w,x,y,z Eigen::Matrix3d rot_mat_t_tt = quat_t_tt.toRotationMatrix(); Eigen::Translation3d trans_t_tt(0, 0, 0); Tt_tt_ = trans_t_tt * rot_mat_t_tt; //不进行旋转,在x负方向平移-0.21米 Eigen::Quaterniond quat_car(1, 0, 0, 0); // w,x,y,z Eigen::Matrix3d rot_car = quat_car.toRotationMatrix(); Eigen::Translation3d trans_car(-0.21, 0, 0); T_car_ = trans_car * rot_car; } TagStationDetection::~TagStationDetection() { } bool TagStationDetection::OpenCam(int cam_id) { LINFO(TagStationDetectionTask, "Enabling video capture"); cap_ = cv::VideoCapture(cam_id); cap_.set(cv::CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, img_width_); cap_.set(cv::CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, img_height_); cv::TickMeter meter; meter.start(); if (!cap_.isOpened()) { LERROR(TagStationDetectionTask, "Couldn't open video capture device"); return false; } else { meter.stop(); LINFO(TagStationDetectionTask, "Detector initialized in " << meter.getTimeSec() << "s" << ", " << cap_.get(cv::CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH) << "x" << cap_.get(cv::CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT) << " @" << cap_.get(cv::CAP_PROP_FPS) << "FPS"); meter.reset(); return true; } } void TagStationDetection::ReleaseCam() { cap_.release(); cv::destroyAllWindows(); } bool TagStationDetection::OpenVideo(const std::string &video_name) { cap_.open(video_name.c_str()); if (!cap_.isOpened()) { std::cerr << "Couldn't open video " << video_name.c_str() << std::endl; return false; } else return true; } bool TagStationDetection::DetectCamFrameTag(TagPose &tag_pose) { bool if_found = false; cap_ >> frame_; if (frame_.empty()) return if_found; if (TAG_IMG_UNDISTORT) { cv::Mat UndistortImage; remap(frame_, UndistortImage, map1_, map2_, cv::INTER_LINEAR);//去畸变 frame_ = UndistortImage; } cvtColor(frame_, gray_, cv::COLOR_BGR2GRAY); image_u8_t im = {.width = gray_.cols, .height = gray_.rows, .stride = gray_.cols, .buf = gray_.data};//转为apriltag库的格式 zarray_t *detections = apriltag_detector_detect(td_, &im);//检测tag /*typedef struct apriltag_detection apriltag_detection_t; struct apriltag_detection { apriltag_family_t *family; int id;//tag的id int hamming; float decision_margin; matd_t *H; //代表从(-1,1), (1,1), (1,-1),(-1,-1)转到像素坐标 double c[2]; //tag中心点在像素坐标下的坐标 double p[4][2]; //像素坐标下的坐标,4个点从左下角开始逆时针旋转 };*/ for (int i = 0; i < zarray_size(detections); i++) { apriltag_detection_t *det; zarray_get(detections, i, &det); if (det->id == 0)//第0个tag { if (det->decision_margin > 50.0) { if_found = true; info_.det = det; apriltag_pose_t pose; // pose origin : center of tag //使用apriltag自带的库求解。这就会涉及库的坐标系和我们的坐标系转换 /*apriltag_detection_info_t tag_info; tag_info.cx=cameraParam.m_cx; tag_info.cy=cameraParam.m_cy; tag_info.fx=cameraParam.m_fx; tag_info.fy=cameraParam.m_fy; tag_info.tagsize=find_mark.length; tag_info.det=det; apriltag_pose_t pose; estimate_tag_pose(&tag_info, &pose); Vector3d ori_relative_P; Matrix3d ori_rotation_matrix3d; memcpy(&ori_relative_P, pose.t->data, sizeof(Vector3d)); memcpy(&ori_rotation_matrix3d, pose.R->data, sizeof(Matrix3d));*/ double err = estimate_tag_pose(&info_, &pose); CalculatePose(pose, tag_pose); if (APRILTAG_DETECTED_IMG_VISUALIZATION) DetectedVisualization(det); } break; } else continue; } if (not if_found) { if (APRILTAG_DETECTED_IMG_VISUALIZATION) DetectedVisualization(); } apriltag_detections_destroy(detections); return if_found; } bool TagStationDetection::DetectImg(const std::string &img_name, TagPose &tag_pose) { bool if_found = false; cv::Mat imge_raw = cv::imread(img_name.c_str()); if (TAG_IMG_UNDISTORT) { cv::Mat UndistortImage; remap(imge_raw, UndistortImage, map1_, map2_, cv::INTER_LINEAR); // cv::imwrite("UndistortImage.png", UndistortImage); frame_ = UndistortImage; } else frame_ = imge_raw; cvtColor(frame_, gray_, cv::COLOR_BGR2GRAY); image_u8_t im = {.width = gray_.cols, .height = gray_.rows, .stride = gray_.cols, .buf = gray_.data}; zarray_t *detections = apriltag_detector_detect(td_, &im); for (int i = 0; i < zarray_size(detections); i++) { apriltag_detection_t *det; zarray_get(detections, i, &det); if (det->id == 0) { if_found = true; info_.det = det; apriltag_pose_t pose; double err = estimate_tag_pose(&info_, &pose); CalculatePose(pose, tag_pose); if (APRILTAG_DETECTED_IMG_VISUALIZATION) DetectedVisualization(det, 1); break; } else continue; } if (not if_found) LWARN(TagStationDetectionTask, "No effective tag detected"); apriltag_detections_destroy(detections); return if_found; } void TagStationDetection::DetectedVisualization(apriltag_detection_t *det, int d) { line(frame_, cv::Point(det->p[0][0], det->p[0][1]), cv::Point(det->p[1][0], det->p[1][1]), cv::Scalar(0, 0xff, 0), 2); line(frame_, cv::Point(det->p[0][0], det->p[0][1]), cv::Point(det->p[3][0], det->p[3][1]), cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0xff), 2); line(frame_, cv::Point(det->p[1][0], det->p[1][1]), cv::Point(det->p[2][0], det->p[2][1]), cv::Scalar(0xff, 0, 0), 2); line(frame_, cv::Point(det->p[2][0], det->p[2][1]), cv::Point(det->p[3][0], det->p[3][1]), cv::Scalar(0xff, 0, 0), 2); std::cout << "pixel coord: (" << det->p[0][0] << ", " << det->p[0][1] << "); " << " (" << det->p[1][0] << ", " << det->p[1][1] << ")" << std::endl; std::stringstream ss; ss << det->id; cv::String text = ss.str(); int fontface = cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SCRIPT_SIMPLEX; double fontscale = 1.0; int baseline; cv::Size textsize = cv::getTextSize(text, fontface, fontscale, 2, &baseline); putText(frame_, text, cv::Point(det->c[0] - textsize.width / 2, det->c[1] + textsize.height / 2), fontface, fontscale, cv::Scalar(0xff, 0x99, 0), 2); imshow("Tag Detections", frame_); cv::waitKey(d); } void TagStationDetection::DetectedVisualization() { imshow("Tag Detections", frame_); cv::waitKey(1); } void TagStationDetection::CalculatePose(const apriltag_pose_t &pose, TagPose &tag_pose) { // pose.R->data a matrix structure for holding double-precision values with // data in row-major order (i.e. index = row*ncols + col). Eigen::Matrix3d rot_mat_cam_tag = rot_cam_slope_ * (Eigen::Map<Eigen::Matrix3d>(pose.R->data).inverse());//转置 //pose.R->data tag系下camera位置 (pose.R->data).inverse()=(pose.R->data).transpose() Tt_c(-1)=Tc_t Eigen::Vector3d trans_vector = -Eigen::Map<Eigen::Vector3d>(pose.t->data); Eigen::Translation3d translation(trans_vector[0], trans_vector[1], trans_vector[2]); //Translation3d是表示平移的一种形式,构造函数为Translation3d(x,y,z),它可以直接和旋转向量、四元数、旋转矩阵相乘,得到的结果为Affine3d类型 Eigen::Affine3d Tc_t = translation * rot_mat_cam_tag;//相机坐标系下tag位置 -R(-1)*T Eigen::Affine3d T_target; T_target.matrix() = (Tb_c_.matrix() * Tc_t.matrix() * Tt_tt_.matrix()).inverse();//计算tag坐标系下相机的位置 Tb_tt(-1)=Ttt_b Eigen::Vector3d rpy_target = R2ypr(T_target.rotation()); tag_pose.x = T_target.matrix()(0, 3); tag_pose.y = T_target.matrix()(1, 3); tag_pose.yaw = rpy_target(0); Eigen::Affine3d T_target_car; T_target_car.matrix() = T_target.matrix() * T_car_.matrix(); tag_pose.y_car = T_target_car.matrix()(1, 3); std::cout << "pose x,y,z,yaw: " << tag_pose.x << ", " << tag_pose.y << ", " << T_target.matrix()(2, 3) << std::endl; } Eigen::Vector3d TagStationDetection::R2ypr(const Eigen::Matrix3d &R) { Eigen::Vector3d n = R.col(0); Eigen::Vector3d o = R.col(1); Eigen::Vector3d a = R.col(2); Eigen::Vector3d ypr(3); double y = atan2(n(1), n(0)); double p = atan2(-n(2), n(0) * cos(y) + n(1) * sin(y)); double r = atan2(a(0) * sin(y) - a(1) * cos(y), -o(0) * sin(y) + o(1) * cos(y)); ypr(0) = y; ypr(1) = p; ypr(2) = r; return ypr; } void TagStationPub::init() { ctx_ = zmq::context_t{1}; publisher_ = zmq::socket_t(ctx_, zmq::socket_type::pub); publisher_.connect("tcp://127.0.0.1:5555"); } void TagStationPub::TagPosePublish(const TagPose &tag_pose) { pose_2d_.data = tag_pose; Pose2dPublish(); LINFO(TagStationDetectionTask, "pub tag pose (x, y, yaw, y_car): " << pose_2d_.data.x << ", " << pose_2d_.data.y << ", " << pose_2d_.data.yaw << ". " << pose_2d_.data.y_car); } void TagStationPub::TagPosePublish() { pose_2d_.data.x = 15; pose_2d_.data.y = 15; pose_2d_.data.yaw = 15; pose_2d_.data.y_car = 15; Pose2dPublish(); LWARN(TagStationDetectionTask, "no detection, pub: " << pose_2d_.data.x << ", " << pose_2d_.data.y << ", " << pose_2d_.data.yaw << ". " << pose_2d_.data.y_car); } void TagStationPub::Pose2dPublish() { publisher_.send(zmq::str_buffer("/charge_station_detection "), zmq::send_flags::sndmore); zmq::message_t msg(sizeof(pose_2d_)); memcpy(msg.data(), pose_2d_.buffer, sizeof(pose_2d_)); publisher_.send(msg); }
apritag_vision: 充电站与apritag之间进行定位,确定车站与车之间的位置关系
5.算法对比验证,opencvpnp求解
把tag检测的角点进行Pnp求解,角度较小时结果可以,角度大时结果不如正叫迭代法。
cv::Mat TagStationDetection::tag_pos_pnp(double p[4][2], apriltag_pose_t *pose) { std::vector<cv::Point3f> point3d; float half_x = APRILTAG_DETECTED_SIZE / 2.0f; float half_y = APRILTAG_DETECTED_SIZE / 2.0f; // height_target / 2.0; hight 30cm 宽12cm object2d_point.clear(); cv::Point2f points; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { points.x = p[i][0]; points.y = p[i][1]; object2d_point.push_back(points); } point3d.push_back(cv::Point3f(-half_x, half_y, 0)); point3d.push_back(cv::Point3f(half_x, half_y, 0)); point3d.push_back(cv::Point3f(half_x, -half_y, 0)); point3d.push_back(cv::Point3f(-half_x, -half_y, 0)); cv::Mat rot = cv::Mat_<double>(3, 3); cv::Mat trans; cv::Mat Rvec; // Mat cam_matrix = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 578.6274, 0, 334.7460, 0, 576.9578, 214.0938, 0, 0, 1); // 1981.3, -6.2, 684, 0, 2006.7, 504, 0, 0, 1 cv::Mat cam_matrix = (cv::Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 471.33715, 0.0, 437.19435, 0.0, 472.0701, 275.1862, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // 1981.3, -6.2, 684, 0, 2006.7, 504, 0, 0, 1 // cv::Mat cam_matrix = cv::Mat_<double>(3, 3); // Mat distortion_coeff = (Mat_<double>(5, 1) << -0.4290, 0.2780, 0, 0, 0); //-0.1029, 0.0058, -0.0030, 0.0047,0 cv::Mat distortion_coeff = (cv::Mat_<double>(5, 1) << -0., 0.060122, -0.000640, 0.001716, 0.000000); cv::solvePnP(point3d, object2d_point, cam_matrix, distortion_coeff, rot, trans, false, CV_EPNP); // CV_P3P); // CV_EPNP); cv::Mat inliers; // solvePnPRansac(point3d, object2d_point, cam_matrix, distortion_coeff, rot, trans, false, 50, 2, 0.98, inliers, 0); // std::cout << "rot size is:" << rot.size() << rot << std::endl; // std::cout << "trans size is:" << trans.size() << std::endl; cv::Mat RR; double rm[9]; RR = cv::Mat(3, 3, CV_64FC1, rm); cv::Rodrigues(rot, RR); double tx = trans.at<double>(0, 0); double ty = trans.at<double>(1, 0); double tz = trans.at<double>(2, 0); double dis = sqrt(tx * tx + ty * ty + tz * tz); pose->R = matd_create(3, 3); for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { MALL(pose->R, i, j) = RR.at<double>(i, j); // zhuanzhi } } pose->t = matd_create(3, 1); for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { MALL(pose->t, i, 0) = trans.at<double>(i, 0); } return trans; }6.PNP求解验证
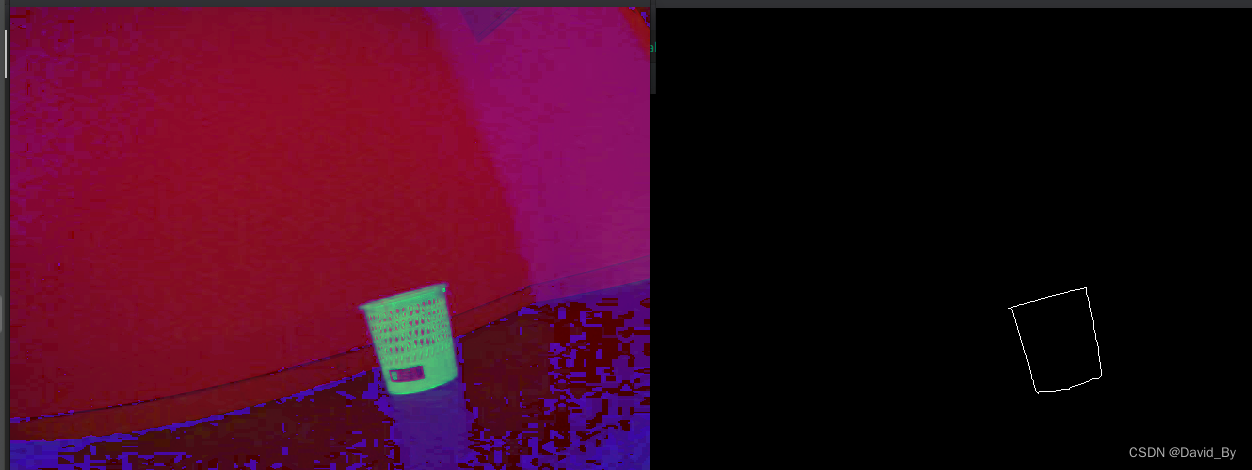


实现代码,检测蓝色物体,尺寸25.6 25.6
#include <opencv2/core.hpp> #include <opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp> #include <opencv2/highgui.hpp> #include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp" #include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp> #include <iostream> using namespace cv; using namespace std; void drawRotatedRect(cv::Mat &img, const cv::RotatedRect &rect, const cv::Scalar &color, int thickness) { cv::Point2f Vertex[4]; rect.points(Vertex); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { cv::line(img, Vertex[i], Vertex[(i + 1) % 4], color, thickness); } } void getTarget2dPoints(cv::RotatedRect object_rect, std::vector<Point2f> &object2d_point) { cv::Point2f vertices[4]; object_rect.points(vertices); cv::Point2f lu, ld, ru, rd; std::sort(vertices, vertices + 4, [](const cv::Point2f &p1, const cv::Point2f &p2) { return p1.x < p2.x; }); if (vertices[0].y < vertices[1].y) { lu = vertices[0]; ld = vertices[1]; } else { lu = vertices[1]; ld = vertices[0]; } if (vertices[2].y < vertices[3].y) { ru = vertices[2]; rd = vertices[3]; } else { ru = vertices[3]; rd = vertices[2]; } object2d_point.clear(); object2d_point.push_back(lu); object2d_point.push_back(ru); object2d_point.push_back(rd); object2d_point.push_back(ld); } // 红 /* int iLowH = 156; int iLowS = 43; int iLowV = 46; int iHighH = 180; int iHighS = 255; int iHighV = 255;*/ // 黑 /* int iLowH = 0; int iLowS = 0; int iLowV = 0; int iHighH = 180; int iHighS = 255; int iHighV = 46;*/ // 橙 /*int iLowH = 11; int iLowS = 43; int iLowV = 46; int iHighH = 25; int iHighS = 255; int iHighV = 255;*/ // 白 /*int iLowH = 0; int iLowS = 0; int iLowV = 221; int iHighH = 180; int iHighS = 30; int iHighV = 255;*/ // 红 /*int iLowH = 156; int iLowS = 43; int iLowV = 46; int iHighH = 180; int iHighS = 255; int iHighV = 255;*/ // 蓝 int iLowH = 100; int iLowS = 43; int iLowV = 46; int iHighH = 124; int iHighS = 255; int iHighV = 255; // 灰 /* int iLowH = 0; int iLowS = 0; int iLowV = 46; int iHighH = 180; int iHighS = 43; int iHighV = 220;*/ int main() { cv::VideoCapture cap(2); Mat gray; Mat binImg; Mat hsv_img; Mat imgThresholded; cv::Mat frame; if (!cap.isOpened()) { return 1; } while (true) { cap >> frame; cvtColor(frame, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY); threshold(gray, binImg, 40, 255, THRESH_BINARY_INV); vector<vector<cv::Point>> bin_contours; cvtColor(frame, hsv_img, COLOR_BGR2HSV); inRange(hsv_img, Scalar(iLowH, iLowS, iLowV), Scalar(iHighH, iHighS, iHighV), imgThresholded); // Threshold the image // blur(imgThresholded,imgThresholded,Size(5,5)); // 开操作 (去除一些噪点) 如果二值化后图片干扰部分依然很多,增大下面的size Mat element = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(5, 5)); morphologyEx(imgThresholded, imgThresholded, MORPH_OPEN, element); // 开运算:先腐蚀后膨胀。 能够排除小亮点。 // 闭运算:先膨胀后腐蚀。能够排除小黑点。 // 闭操作 (连接一些连通域) morphologyEx(imgThresholded, imgThresholded, MORPH_CLOSE, element); erode(imgThresholded, imgThresholded, element); // 腐蚀 binImg = imgThresholded; vector<Vec4i> hierarchy; cv::findContours(binImg, bin_contours, hierarchy, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point()); Mat imageContours = Mat::zeros(binImg.size(), CV_8UC1); Mat Contours = Mat::zeros(binImg.size(), CV_8UC1); // 绘制 for (uint i = 0; i < bin_contours.size(); i++) { for (int j = 0; j < bin_contours[i].size(); j++) { // 绘制出contours向量内所有的像素点 Point P = Point(bin_contours[i][j].x, bin_contours[i][j].y); Contours.at<uchar>(P) = 255; } drawContours(imageContours, bin_contours, i, Scalar(255), 1, 8, hierarchy); cv::RotatedRect RRect = minAreaRect(bin_contours[i]); std::cout << "rect_size:" << RRect.size.area() << std::endl; /*if (RRect.size.area() < 200 || RRect.size.area() > ) continue; if (max(RRect.size.width, RRect.size.height) / min(RRect.size.width, RRect.size.height) > 1.3) continue;*/ if (RRect.size.area() < 2000) continue; drawRotatedRect(frame, RRect, cv::Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2); // 画出红色大于200的矩形 Mat rot_vector, translation_vector; vector<Point2f> object2d_point; getTarget2dPoints(RRect, object2d_point); std::vector<cv::Point3f> point3d; float half_x = 25.6f / 2.0f; float half_y = 25.6f / 2.0f; // height_target / 2.0; hight 30cm 宽12cm point3d.push_back(Point3f(-half_x, half_y, 0)); point3d.push_back(Point3f(half_x, half_y, 0)); point3d.push_back(Point3f(half_x, -half_y, 0)); point3d.push_back(Point3f(-half_x, -half_y, 0)); cv::Mat rot; cv::Mat trans; // Mat cam_matrix = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 578.6274, 0, 334.7460, 0, 576.9578, 214.0938, 0, 0, 1); // 1981.3, -6.2, 684, 0, 2006.7, 504, 0, 0, 1 Mat cam_matrix = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 471.33715, 0.0, 437.19435, 0.0, 472.0701, 275.1862, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // 1981.3, -6.2, 684, 0, 2006.7, 504, 0, 0, 1 // Mat distortion_coeff = (Mat_<double>(5, 1) << -0.4290, 0.2780, 0, 0, 0); //-0.1029, 0.0058, -0.0030, 0.0047,0 Mat distortion_coeff = (Mat_<double>(5, 1) << -0., 0.060122, -0.000640, 0.001716, 0.000000); cv::solvePnP(point3d, object2d_point, cam_matrix, distortion_coeff, rot, trans); std::cout << "rot size is :" << rot.size() << std::endl; // void solvePnP(InputArray objectPoints, InputArray imagePoints, InputArray cameraMatrix, InputArray distCoeffs, OutputArray rvec, OutputArray tvec, bool useExtrinsicGuess=false, int flags = CV_ITERATIVE) // objectPoints - 世界坐标系下的控制点的坐标,vector<Point3f> 的数据类型在这里可以使用 // imagePoints - 在图像坐标系下对应的控制点的坐标。vector<Point2f> 在这里可以使用 // cameraMatrix - 相机的内参矩阵 distCoeffs - 相机的畸变系数 double tx = trans.at<double>(0, 0); double ty = trans.at<double>(1, 0); double tz = trans.at<double>(2, 0); double dis = sqrt(tx * tx + ty * ty + tz * tz); cout << "dis:" << dis << "tx:" << tx << "ty:" << ty << "tz:" << tz << endl; cv::putText(frame, to_string(dis) + "cm", Point(50, 50), 1, 2, Scalar(0, 255, 100), 2); cv::putText(frame, to_string(tz) + "cm", Point(300, 50), 1, 2, Scalar(0, 255, 100), 2); cv::putText(frame, to_string(tx) + "cm", Point(50, 100), 1, 2, Scalar(0, 255, 100), 2); } imshow("1", frame); imshow("3", hsv_img); imshow("2", imgThresholded); imshow("4", imageContours); if (waitKey(10) == 'q') break; } } 7.PNP求解BA迭代
PnP(Perspective-n-Point)问题:各种算法总结分析 - 知乎
光束法平差(BA,Bundle Adjustment):与正交迭代法相同
上面的方法都是线性的,我们还可以把PnP问题构建为一个关于重投影误差的非线性最小二乘问题。线性方法往往是通过将空间点的位置看做已知量,通过构建方程组求解相机位姿。而非线性优化则将相机位姿和空间点位置都看成优化变量,放在一起优化,这也是BA的另一个名字:捆集优化的由来(个人理解)。这种方法将相机位姿和三维点位置放在一起进行重投影误差最小化的优化,是一种整体的优化方法。


void bundleAdjustmentGaussNewton( const VecVector3d &points_3d, const VecVector2d &points_2d, const Mat &K, Sophus::SE3d &pose) { //传入空间点点,空间点像素坐标,内参; 初始pose,此程序中初始pose为0; typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> Vector6d; const int iterations = 10; double cost = 0, lastCost = 0; double fx = K.at<double>(0, 0); double fy = K.at<double>(1, 1); double cx = K.at<double>(0, 2); double cy = K.at<double>(1, 2); for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++) { //进行迭代 Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6> H = Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6>::Zero(); Vector6d b = Vector6d::Zero(); cost = 0; // compute cost for (int i = 0; i < points_3d.size(); i++) { Eigen::Vector3d pc = pose * points_3d[i];//得到空间点在相机坐标系下的坐标 // Vector6d se3 = pose.log(); // cout<<"se3 = "<<se3.transpose()<<endl;一开始se3为0,三四次迭代后趋于稳定 double inv_z = 1.0 / pc[2]; double inv_z2 = inv_z * inv_z; Eigen::Vector2d proj (fx * pc[0] / pc[2] + cx, fy * pc[1] / pc[2] + cy);//P点像素坐标 //的投影计算值 Eigen::Vector2d e = points_2d[i] - proj;//作差,得到差值;是观测值-预测值! cost += e.squaredNorm();//误差的二范数的平方 Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 6> J;//2*6的雅克比矩阵,即误差相对于位姿求导,通过导数可以知道有了误 //差以后我们应该往哪个方向去优化 J << -fx * inv_z, 0, fx * pc[0] * inv_z2, fx * pc[0] * pc[1] * inv_z2, -fx - fx * pc[0] * pc[0] * inv_z2, fx * pc[1] * inv_z, 0, -fy * inv_z, fy * pc[1] * inv_z, fy + fy * pc[1] * pc[1] * inv_z2, -fy * pc[0] * pc[1] * inv_z2, -fy * pc[0] * inv_z; H += J.transpose() * J;//高斯牛顿方法,H*dx=b b += -J.transpose() * e; } Vector6d dx; dx = H.ldlt().solve(b);//对H做LDLT分解,并求解dx cout <<"dx:" << endl << dx <<endl; cout <<"dx.norm():" << endl << dx.norm() <<endl; if (isnan(dx[0])) { cout << "result is nan!" << endl; break; } if (iter > 0 && cost >= lastCost) { // cost increase, update is not good//发散的情况 cout << "cost: " << cost << ", last cost: " << lastCost << endl; break; } // update your estimation pose = Sophus::SE3d::exp(dx) * pose; lastCost = cost; cout << "iteration " << iter << " cost=" << cout.precision(12) << cost << endl; if (dx.norm() < 1e-6) { // converge 当dx<1e-6时停止迭代 break; } } cout << "pose by g-n: \n" << pose.matrix() << endl; }每种算法用一句话概括:
- DLT:根据n个点的世界坐标和相机归一化平面坐标,最后一行用于消去深度,得到2n个约束方程,利用SVD求解超定方程并得到位姿矩阵的估计。
- P3P:根据3个点的世界坐标和相机归一化平面坐标,利用余弦定理几何关系,得到3个点的相机坐标,将问题转化为3D-3D位姿估计并利用ICP求解,最后还需要一对点用于验证。
- EPnP:根据n个点的世界坐标选择4个控制点并计算加权系数,通过相机模型和n个点的像素坐标求解4个控制点在相机坐标系下的坐标,进而得到n个点在相机坐标系下的坐标,将问题转化为3D-3D位姿估计并利用ICP求解。
- BA:根据对应点的重投影误差构建非线性优化问题,利用李代数得到误差关于位姿的导数以指导优化方向,不断迭代求得所有对应点重投影误差之和最小的位姿估计。








版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容,请联系我们,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://51itzy.com/kjqy/44634.html