目录
一、问题定义
二、定义对象
三、判断能否观察到
四、**观测时间
1.气团
2.视差角
3.天空图
五、完整代码及注释
一、问题定义
假设我们要使用斯巴鲁(subaru)望远镜观察“夏季大三角”(Altair,Deneb和Vega)。
二、定义对象
1.首先,定义一个Observer对象,代表subaru望远镜。
from astroplan import Observer subaru = Observer.at_site('subaru')2.然后,定义FixedTarget,即所要观察的目标。
①因为夏季三角形相对于天球是固定的(如果忽略相对较小的适当运动)。我们将使用from_name类方法,该方法在CDS名称解析器中查询目标的坐标
讯享网from astropy.coordinates import SkyCoord from astroplan import FixedTarget altair = FixedTarget.from_name('Altair') vega = FixedTarget.from_name('Vega')
②对于无法使用from_name解析的对象,可以手动输入坐标
coordinates = SkyCoord('20h41m25.9s', '+45d16m49.3s', frame='icrs') #20h41m25.9s是赤经,+45d16m49.3s是赤纬 deneb = FixedTarget(name='Deneb', coord=coordinates)3.定义一个我们希望观察的时间Time(以UTC为单位)
讯享网from astropy.time import Time time = Time('2015-06-16 12:00:00') #夏季UTC时间,当地凌晨2点
三、判断能否观察到
1.判断我们是否能观察到目标,也就是太阳落山的时候这3个目标是否在地平线上方

subaru.target_is_up(time, altair) subaru.target_is_up(time, vega) subaru.target_is_up(time, deneb) 2.判断太阳是否落下
subaru.is_night(time)3.由于升起和落下计算的进度限制,我们手动适当调整一下升起和落下的时间。
import numpy as np import astropy.units as u altair_rise = subaru.target_rise_time(time, altair) + 5*u.minute altair_set = subaru.target_set_time(time, altair) - 5*u.minute vega_rise = subaru.target_rise_time(time, vega) + 5*u.minute vega_set = subaru.target_set_time(time, vega) - 5*u.minute deneb_rise = subaru.target_rise_time(time, deneb) + 5*u.minute deneb_set = subaru.target_set_time(time, deneb) - 5*u.minute all_up_start = np.max([altair_rise, vega_rise, deneb_rise]) all_up_end = np.min([altair_set, vega_set, deneb_set])4.让我们找到今晚的日落和日出(并确认它们确实是今晚的)
# 日落 sunset_tonight = subaru.sun_set_time(time, which='nearest') print(sunset_tonight.iso) # 日出 sunrise_tonight = subaru.sun_rise_time(time, which='nearest') print(sunrise_tonight.iso)5.检查日落和日出, 并定义观察窗口的界限
start = np.max([sunset_tonight, all_up_start]) print(start.iso) end = np.min([sunrise_tonight, all_up_end]) print(end.iso) 四、**观测时间
1.气团
①为了在观察的夜晚大致了解目标的气团,我们可以在夜间进行绘制
from astroplan.plots import plot_airmass import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plot_airmass(altair, subaru, time) plot_airmass(vega, subaru, time) plot_airmass(deneb, subaru, time) plt.legend(loc=1, bbox_to_anchor=(1, 1)) plt.show()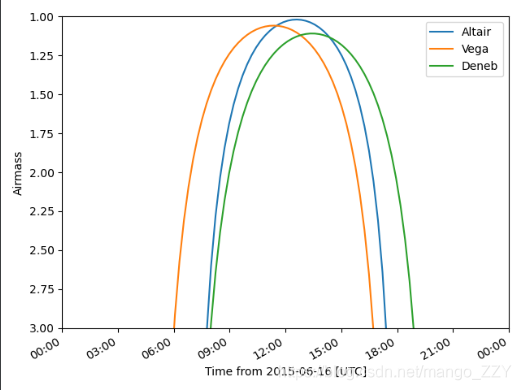
②获取空气质量
subaru.altaz(time, altair).secz subaru.altaz(time, vega).secz subaru.altaz(time, deneb).secz 2.视差角
①为了在观察之夜大致了解目标的视差角,我们可以绘制另一个绘图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from astroplan.plots import plot_parallactic plot_parallactic(altair, subaru, time) plot_parallactic(vega, subaru, time) plot_parallactic(deneb, subaru, time) plt.legend(loc=2) plt.show()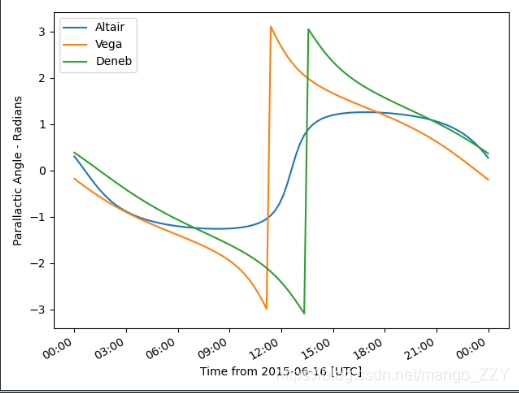
3.天空图
①上面我们已经确定了观察目标的时间范围,现在来确定一下在时间窗的开始和结束时,目标在天空中的位置
from astroplan.plots import plot_sky import matplotlib.pyplot as plt altair_style = {'color': 'r'} deneb_style = {'color': 'g'} plot_sky(altair, subaru, start, style_kwargs=altair_style) plot_sky(vega, subaru, start) plot_sky(deneb, subaru, start, style_kwargs=deneb_style) plt.legend(loc='center left', bbox_to_anchor=(1.25, 0.5)) plt.show() plot_sky(altair, subaru, end, style_kwargs=altair_style) plot_sky(vega, subaru, end) plot_sky(deneb, subaru, end, style_kwargs=deneb_style) plt.legend(loc='center left', bbox_to_anchor=(1.25, 0.5)) plt.show()开始时:
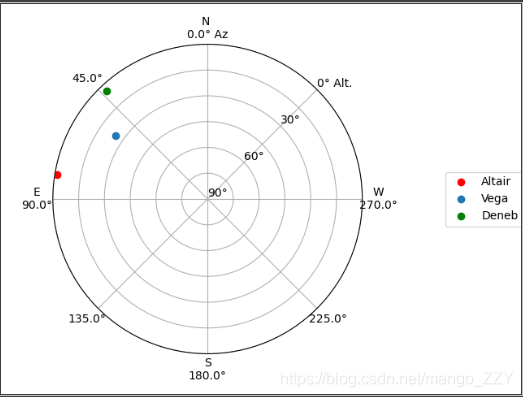
结束时:
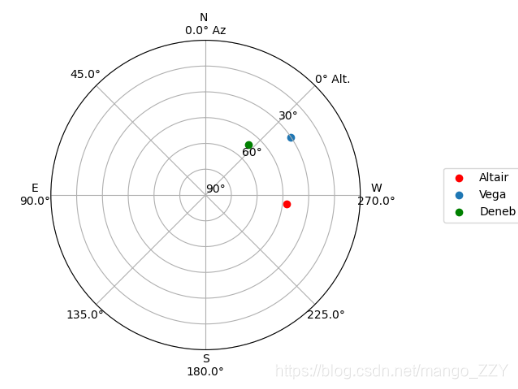
注意:如果出现了此错误,不要慌。这是因为源代码只支持matplotlib<3.3版本,我删除了3.3.3版本又重新安装了3.2.1版本,就可以消除错误了。
ValueError: The number of FixedLocator locations (8), usually from a call to set_ticks, does not match the number of ticklabels (7).
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容,请联系我们,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://51itzy.com/kjqy/28013.html