问题描述 :
实验目的:学习友元的使用。
实验内容:
定义一个Point类,包括两个私有成员:int x, int y,它们分别表示一个点的x和y座标。
再定义构造函数:
Point(int x, int y),即传两个参数,构造一个点对象。
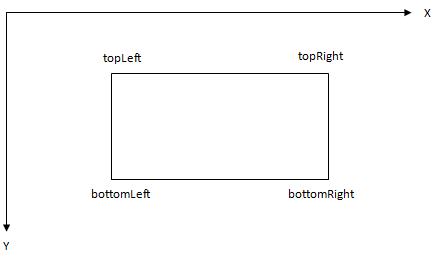
定义一个Rectangle类,包括4个私有成员:Point topLeft, topRight,bottomLeft, bottomRight,它们分别表示长方形4个顶点的座标。
注意:在计算机系统里,座标系如下定义:屏幕的左上角的座标是(0,0),x轴是横轴,屏幕的最右端x值最大,y轴是纵轴,屏幕的最下方y值最大。图如下:
再定义构造函数:
Rectangle(Point topLeft, Point topRight, Point bottomLeft, Point bottomRight)
以及实例方法:
bool isRectangle() //判断4个顶点构成的图形是不是长方形,是则返回true,否则返回false。这个方法只在本类中调用,所以可声明为private的。
int getArea() //如果是长方形则返回长方形的面积,否则返回0
bool isIn(Point p) //如果是长方形则判断传入的点是否在该图形之内(不包括边界),如果在内部返回true,不在内部则返回false。如果不是长方形,则一律返回false。
说明:由于在Rectangle类中有大量的语句需要使用到Point类的私有成员x和y,因此,使用友元可直接访问x和y,从而可减少编程中的麻烦。

使用main函数测试以上getArea方法和isIn方法。main函数可参考如下代码:
int main()
{
int topLeftX, topLeftY, topRightX, topRightY, bottomLeftX, bottomLeftY, bottomRightX, bottomRightY;
int px, py;
Point p(px, py);
Rectangle r(Point(topLeftX, topLeftY), Point(topRightX, topRightY), Point(bottomLeftX, bottomLeftY), Point(bottomRightX, bottomRightY));
cout << r.getArea() << endl;
if (r.isIn(p))
cout << "In" << endl;
else
cout << "Not in" << endl;
输入说明 :
第一行输入长方形r的信息,包括四个顶点x座标及y座标,顶点的输入顺序为左上、右上、左下、右下。
第二行输入一个点p的信息,包括其x座标和y座标。
所有输入都为非负整数,之间以一个空格分隔。无多余空格或空行。
输出说明 :
输出两行,第一行输出长方形面积,第二行输出点p是否位于长方形r之内,如果在内部,则输出“In”,否则输出“Not in”。
输入范例 :
输出范例 :
解题代码:
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cmath> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<map> #include<algorithm> #include<set> #include<vector> #include<queue> using namespace std; class Point { private: int x; int y; public: Point(int x, int y); Point(void); int get_x(); int get_y(); friend class Rectangle; }; Point::Point(int x, int y) { Point::x = x; Point::y = y; } Point::Point(void) { ; } int Point::get_x() { return x; } int Point::get_y() { return y; } class Rectangle { private: Point topLeft; Point topRight; Point bottomLeft; Point bottomRight; int l, r; bool yorn; //判断4个顶点构成的图形是不是长方形,是则返回true,否则返回false。这个方法只在本类中调用,所以可声明为private的 bool isRectangle(); public: Rectangle(Point topLeft, Point topRight, Point bottomLeft, Point bottomRight); Rectangle(); int getArea(); //如果是长方形则返回长方形的面积,否则返回0 bool isIn(Point p);//如果在内部返回true,不在内部则返回false。如果不是长方形,则一律返回false。 }; Rectangle::Rectangle(Point topLeft, Point topRight, Point bottomLeft, Point bottomRight) { Rectangle::topLeft = topLeft; Rectangle::topRight = topRight; Rectangle::bottomLeft = bottomLeft; Rectangle::bottomRight = bottomRight; l = topRight.x - topLeft.x; r = bottomRight.y - topRight.y; //cout << "vd=" << topRight.y <<" "<< topLeft.y << endl; //cout << l << " " << r << endl; if (isRectangle()) yorn = 1;//1-长方形 0-NO else yorn = 0; //cout << yorn << endl; } Rectangle::Rectangle() { ; } bool Rectangle::isRectangle() { if (l == r) { return 0; } if((topRight.x-topLeft.x)==(bottomRight.x-bottomLeft.x)) ; else return 0; if((bottomLeft.y-topLeft.y)==(bottomRight.y-topRight.y)) ; else return 0; return 1; } int Rectangle::getArea() { int ans = 0; if (yorn == 0) return 0; ans = l * r; return ans; } bool Rectangle::isIn(Point p) { bool ok1 = 0, ok2 = 0; if (yorn == 0) return 0; if (topLeft.x< p.x && p.x < topRight.x) ok1 = 1; else ok1 = 0; if (topLeft.y < p.y && p.y < bottomLeft.y) ok2 = 1; else ok2 = 0; return (ok1 && ok2); } int main() { int topLeftX, topLeftY, topRightX, topRightY, bottomLeftX, bottomLeftY, bottomRightX, bottomRightY; int px, py; cin >> topLeftX >> topLeftY >> topRightX >> topRightY >> bottomLeftX >> bottomLeftY >> bottomRightX >> bottomRightY; cin >> px >> py; Point p(px, py); Rectangle r(Point(topLeftX, topLeftY), Point(topRightX, topRightY), Point(bottomLeftX, bottomLeftY), Point(bottomRightX, bottomRightY)); cout << r.getArea() << endl; if (r.isIn(p)) cout << "In" << endl; else cout << "Not in" << endl; return 0; }讯享网

版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容,请联系我们,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://51itzy.com/kjqy/58318.html