封装一个函数 实现能从指定节点插入新节点(可选择从前或从后)
函数原型如下:
struct Test* insertNode(struct Test *p,struct Test *new,int data,char* way) 讯享网
第一个参数是原链表头节点地址
第二个参数是要插入的新节点地址
第三个参数是要插入的节点的位置,用结构体的值来表示(实际项目可自由更改)
第四个参数是插入方式(前:AHEAD / 后:BEHIND)
介绍后插入节点的思路:
一:从前插入:
1.如果是从头节点前插入,则直接令新节点的下一个等于头节点,然后返回新节点即可
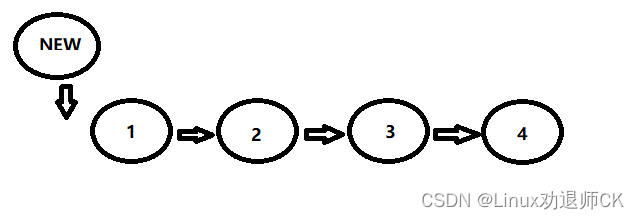
讯享网2.如果不是头节点,则在遍历链表的过程中判断现节点P的下一个节点P->NEXT的值是否是要插入的位置,如果是:
第一步:那么新节点的NEXT等于P->NEXT
第二步:P的NEXT指向新节点。
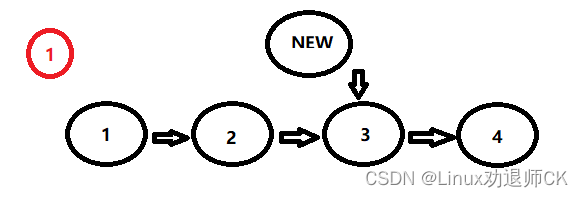
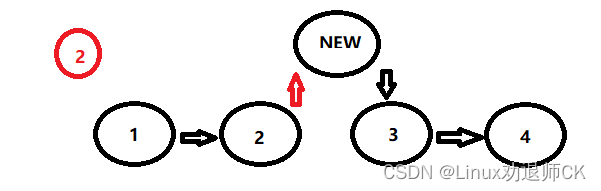 代码如下:
代码如下:
讯享网struct Test* insertNodeAhead(struct Test *p,struct Test *new,int data)//从前插入节点 {
struct Test *head=p; if(head->data==data)//插入在第一个之前 {
new->next=head; return new; } while(p->next!=NULL) {
if(p->next->data==data) {
new->next=p->next; p->next=new; return head; } p=p->next; } printf("no this data:%d\n",data); return head; }
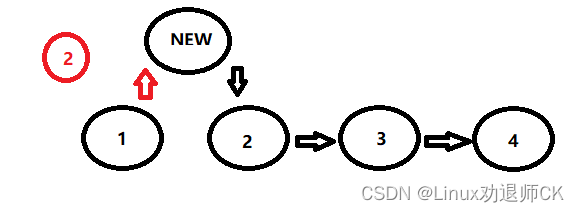
二:从后插入:
从后插入比较简单,只需判断一种情况:
在遍历链表的过程中判断现节点P的值是否是要插入的位置,如果是:
第一步:那么新节点的NEXT等于P->NEXT
第二步:P的NEXT指向新节点。

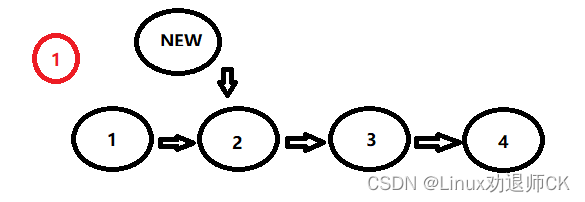
 代码如下:
代码如下:
struct Test* insertNodeBehind(struct Test *p,struct Test *new,int data)//从后插入节点 {
struct Test* head=p; while(p!=NULL) {
if(p->data==data) {
new->next=p->next; p->next=new; return head; } p=p->next; } printf("no this data:%d\n",data); return head; } 整体代码实现如下:
讯享网#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> #define AHEAD "ahead" #define BEHIND "behind" struct Test {
int data; struct Test *next; }; void printLink(struct Test *p) {
while(p!=NULL) {
printf("%d\n",p->data); p=p->next; } } struct Test* insertNodeBehind(struct Test *p,struct Test *new,int data)//从后插入节点 {
struct Test* head=p; while(p!=NULL) {
if(p->data==data) {
new->next=p->next; p->next=new; return head; } p=p->next; } printf("no this data:%d\n",data); return head; } struct Test* insertNodeAhead(struct Test *p,struct Test *new,int data)//从前插入节点 {
struct Test *head=p; if(head->data==data)//插入在第一个之前 {
new->next=head; return new; } while(p->next!=NULL) {
if(p->next->data==data) {
new->next=p->next; p->next=new; return head; } p=p->next; } printf("no this data:%d\n",data); return head; } struct Test* insertNode(struct Test *p,struct Test *new,int data,char* way) {
struct Test *head=p; int ret=-1; if(strstr(way,"behind")!=NULL) {
ret=1; } else if(strstr(way,"ahead")!=NULL) {
ret=0; } switch(ret) {
case 1: head=insertNodeBehind(head,new,data); break; case 0: head=insertNodeAhead(head,new,data); break; default: printf("Parm error\n"); return NULL; } return head; } int main() {
struct Test t1={
1,NULL}; struct Test t2={
2,NULL}; struct Test t3={
3,NULL}; struct Test t4={
4,NULL}; struct Test t5={
5,NULL}; struct Test new1={
8,NULL}; struct Test new2={
0,NULL}; struct Test new3={
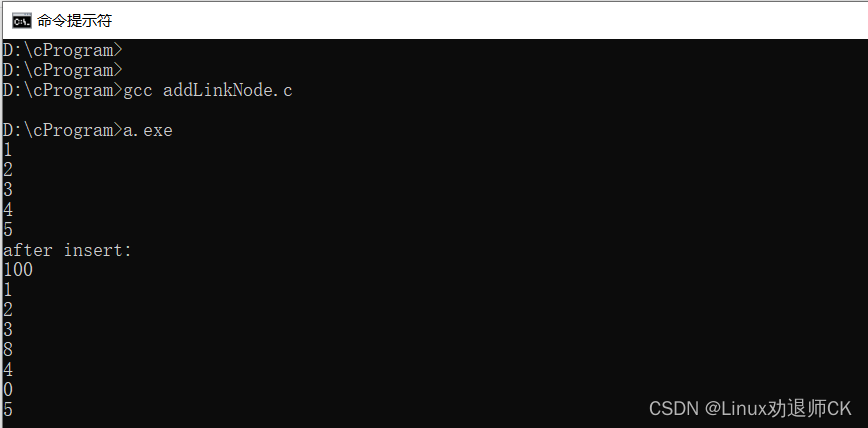
100,NULL}; struct Test *head=&t1; t1.next=&t2; t2.next=&t3; t3.next=&t4; t4.next=&t5; printLink(head); head=insertNode(head,&new1,3,BEHIND); head=insertNode(head,&new2,5,AHEAD); head=insertNode(head,&new3,1,AHEAD); printf("after insert:\n"); printLink(head); }
运行结果如下:

版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容,请联系我们,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://51itzy.com/kjqy/23498.html